The Power of Topography Mapping in Design Optimisation
A fundamental principle in architecture is to build a harmonious interaction between design and the natural surroundings. Architects, along with surveyors and planners, negotiate the difficulties of this endeavour by using exact data and extensive insights to design structures that blend in with their surroundings while achieving functional needs. At the centre of this endeavour is the essential instrument of topographical mapping.
In the following article, we will discuss the significance of topographical mapping in architectural design, investigating its multifaceted uses, numerous benefits, and vital role in improving the fabric of the built environment.
1m contours are available here
Topography mapping is a detailed representation of a geographical area's physical properties, including elevation, terrain, and structures. These detailed maps give specialists a thorough perspective of the land's contours, allowing them to make informed judgements throughout the planning process.
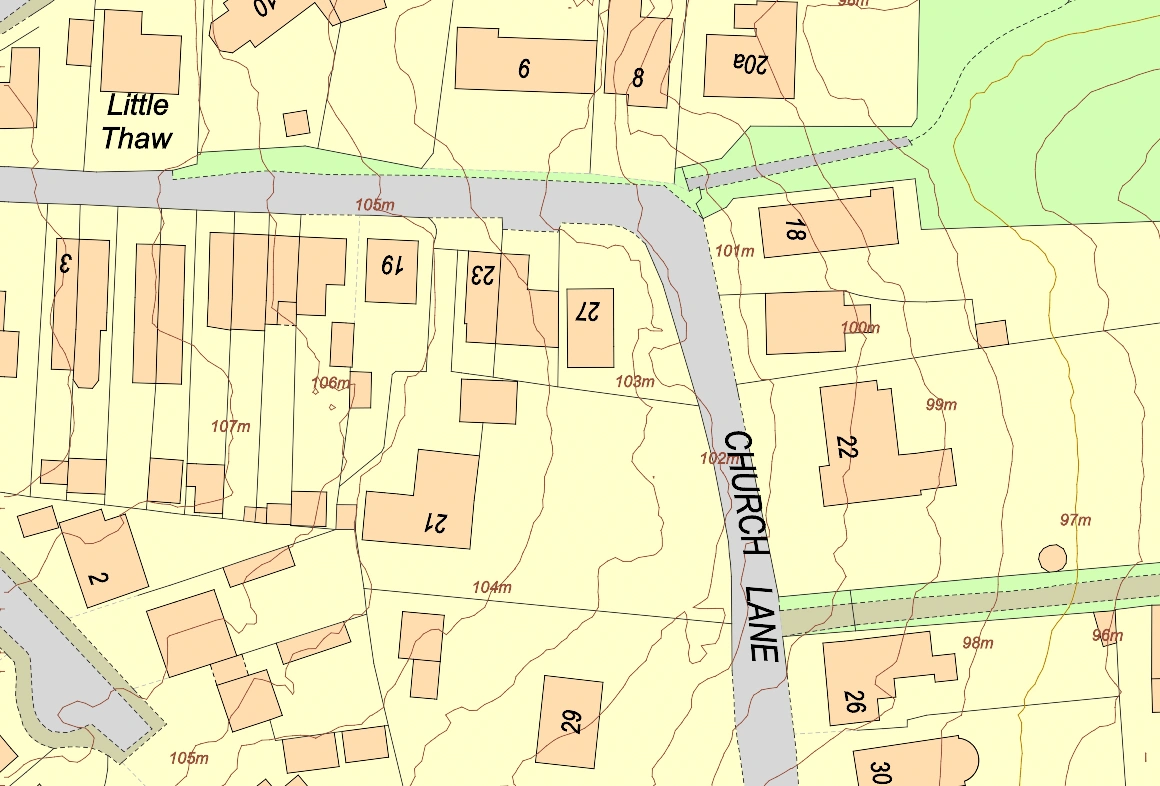
Topographic Map of an urban area using MapServe®'s 1m contours
Uses of Topography Mapping in Architectural Design
Site Analysis
Topography mapping forms the basis for site analysis in architecture projects. Topographic maps provide architects with information about essential aspects such as slopes, drainage patterns, and soil conditions. Understanding these site characteristics enables proactive planning, overcoming probable problems, and optimising site utilisation.
Structural Considerations
Topography mapping plays an important role in architectural design since it acts as a foundation for assuring structural stability. These precisely made maps, which provide realistic portrayals of elevation fluctuations across landscapes, play an important role in assisting architects and engineers in choosing the best locations for building foundations. Using topographical mapping data, professionals can undertake extensive assessments to locate places with stable terrain, reducing the inherent dangers connected with unstable ground conditions. This rigorous planning not only improves the structural integrity of buildings, but it also extends the lifespan of structures by reducing possible hazards. As a result, topographical mapping remains a crucial tool in the armoury of architects and engineers, helping the design of durable and long-lasting architectural structures that withstand the test of time.
Aesthetic Integration
Using topographical mapping in architecture design enhances aesthetic interaction with the natural landscape. By harmonising building placements and landscaping with the contours of the terrain, architects create harmonious habitats that blend in with their surroundings. This strategy not only improves visual attractiveness, but it also creates a sense of connection between the built environment and nature.
Sustainable Design Practices
Topography mapping supports sustainable design methods by supporting resource-efficient solutions and minimising environmental effect. Architects can cut energy consumption and construction waste by taking advantage of natural features and minimising earthmoving. Furthermore, topographic maps can discover prospects for green infrastructure, such as rain gardens and bioswales, which reduce stormwater runoff and increase biodiversity.
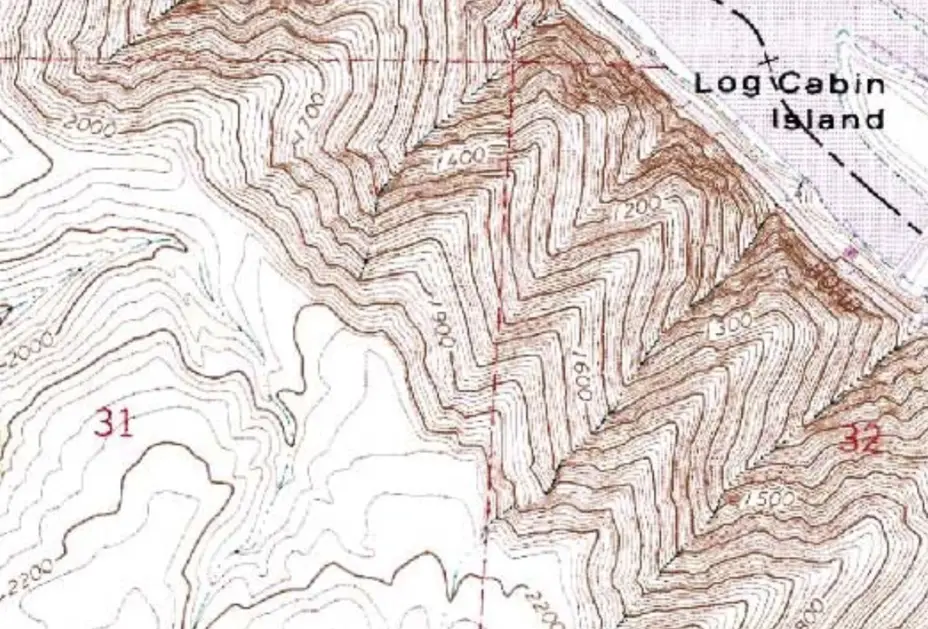
Older Sample of a Topographic Map
The Role of Topography Mapping in Urban Planning
Topography mapping is extremely important in urban planning, providing a wealth of specific information required for strategic development. This data is a valuable resource for architects, allowing them to undertake in-depth analysis of land use patterns and find appropriate places for various forms of development, such as residential, commercial, and industrial projects. Architects may make informed judgements that encourage sustainable development practices while reducing risks by taking into account aspects such as slope and environmental sensitivity. For example, when designing a new residential neighbourhood, topographical mapping provides essential insights into locating construction-friendly locations while avoiding areas prone to flooding or environmental risks. This guarantees that architectural designs are not only aesthetically beautiful, but also durable and environmentally responsible, resulting in lively and living urban areas.
Collaborative Approaches for Sustainable Cities
Topography mapping provides a foundation for collaborative methods for developing sustainable cities. Architects, surveyors, planners, and policymakers work together to create urban landscapes that prioritise efficient land use, environmental conservation, and resident well-being. Topographic data analysis helps stakeholders identify viable development locations while maintaining natural habitats and green spaces. They also take steps to conserve fragile ecosystems and strengthen urban resilience to environmental threats. This collaborative effort includes developing urban environments that promote pedestrian-friendly layouts, access to green spaces, and efficient transportation systems, thereby improving inhabitants' quality of life. Professionals use topography mapping to encourage community action in developing vibrant and habitable cities that meet the complex concerns of urbanisation while assuring sustainability for future generations.
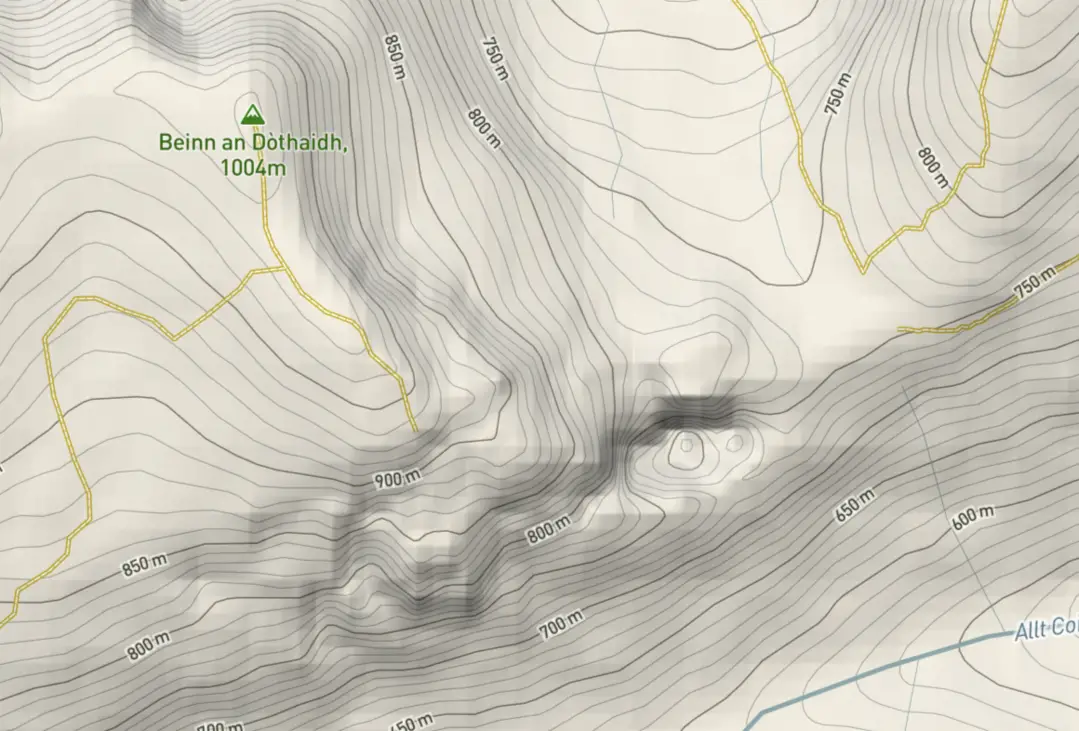
Topographic Map of an area in the Highlands of Scotland by TopoMap
Benefits of Topography Mapping
Accuracy and Precision
Topographic maps are vital resources for architects and planners in the United Kingdom, providing precise and accurate data required for informed decision-making and proactive design management. By giving precise elevation, topographical features, and land characteristics, these maps allow professionals to predict probable design issues and optimise project planning. Topographic maps, for example, can help identify locations prone to flooding or landslides in urban development projects such as London or Manchester, allowing architects and planners to put suitable mitigation measures in place.
Furthermore, accurate topographic mapping ensures that projects be completed efficiently, reducing the need for costly revisions and delays. In a landscape as diverse and physically diversified as the United Kingdom, whose terrain can range from rolling hills to steep valleys, topographic maps are critical in ensuring that architectural projects are customised to their individual settings, thereby improving safety and cost-effectiveness.
Enhanced Safety
In the context of architectural and construction projects in the United Kingdom, topographical mapping emerges as an essential tool for architects, surveyors, and planners, providing crucial insights into potential dangers and risks linked with site conditions. Professionals can detect places prone to geological hazards such as landslides, subsidence, or flooding by methodically analysing topographic data, which is especially important in locations like coastal erosion-prone zones or mountainous terrain prone to slope instability. Armed with this knowledge, architects and planners may devise proactive risk-mitigation techniques that ensure occupant and structural safety.
In heavily populated urban regions such as London, where underground infrastructure and historical geological features may cause problems, topographical mapping can help detect potential hazards and develop appropriate foundation systems and structural reinforcements. Furthermore, in rural areas with different landscapes, such as the Scottish Highlands or the Welsh lowlands, topography mapping aids in the identification of natural features like as watercourses or geological faults that may affect site stability.
Cost Savings
In the dynamic environment of architectural and construction projects in the United Kingdom, the strategic use of topographical mapping emerges as a cornerstone for delivering significant cost savings throughout the project lifetime. Architects, surveyors, and planners use topographic data to rigorously analyse site characteristics, allowing them to apply cost-effective techniques that reduce earthmoving while optimising site utilisation. For example, in urban redevelopment projects in locations such as Birmingham and Bristol, where land availability is limited and construction prices are high, topographical mapping helps to identify ideal building placements and efficient land use techniques. By strategically positioning structures and infrastructure in accordance with natural curves and features, architects can eliminate the need for major earthmoving and grading, saving construction costs and increasing return on investment for their clients.
Furthermore, in environmentally sensitive areas such as national parks or conservation zones such as the Lake District or the Peak District, topography mapping aids in identifying ecologically sensitive areas and designing low-impact development strategies that preserve natural habitats while reducing construction costs. Architects and planners can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining project quality and sustainability by leveraging topographic insights to streamline design processes and optimise resource utilisation, thereby improving the overall economic viability and success of architectural endeavours across the UK.
Improved User Experience
Topographical mapping is critical in influencing the design process for architects, surveyors, and planners. By incorporating topographic data into their designs, professionals can build visually appealing and useful places that improve the entire user experience. Topography mapping, for example, aids architects in integrating structures with the natural landscape, resulting in colourful urban landscapes. Similarly, topographical mapping supports integrated community designs in suburban residential developments such as Surrey and Kent, focusing on pedestrian-friendly layouts and access to green space. Professionals can use topographic knowledge strategically to build places that increase the quality of life for residents and visitors without using excessive rhetoric.
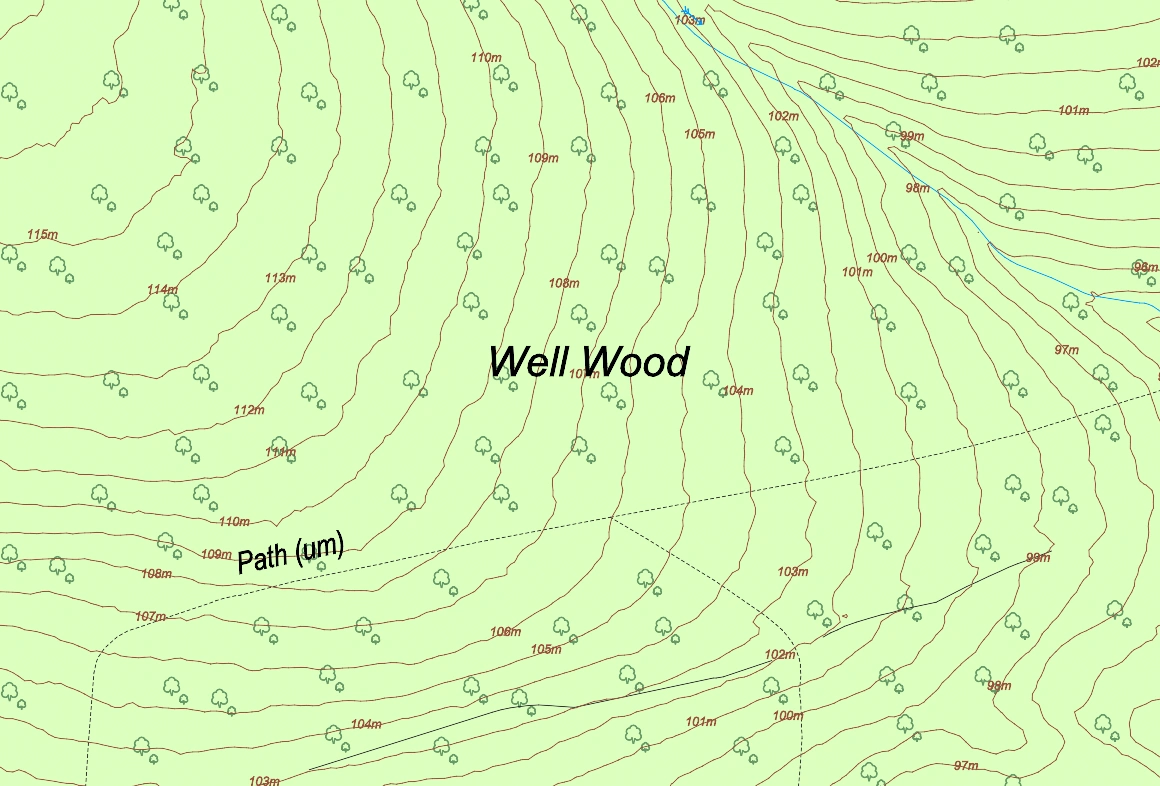
Topographic Map of a forest area using MapServe®'s 1m contours
Topographic mapping develops as a key method to architectural design, providing essential insights that benefit the built environment. Architects, along with surveyors and planners, use precise data produced from topography mapping to create environments that seamlessly blend with their surroundings, improve safety, and promote long-term sustainability through the implementation of sustainable practices. As technological improvements continue, the significance of topographic mapping in architectural design will become ever more important, affecting the built environment for future generations. Professionals may confidently traverse the changing architectural landscape by strategically utilising topographical information, producing places that not only fulfil current demands but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.