The effects of climate change are becoming increasingly evident in the UK with rising sea levels, more frequent heavy rainfall and extreme weather events posing significant risks to infrastructure, homes and communities. Among these challenges, flooding has emerged as one of the most pressing issues for architects, urban planners and the building industry. To address these risks, digital mapping technologies offer innovative and effective solutions for flood risk assessment and prevention.
Access the latest topographical maps
The Growing Importance of Flood Risk Mapping in the UK
Flooding has long been a concern in the UK but climate change has heightened its severity. According to the Environment Agency, 5.2 million properties in England alone are at risk of flooding. The 2020 winter floods and the devastation caused by Storm Ciara and Storm Dennis demonstrated the urgent need for proactive flood management strategies. With predictions suggesting that extreme weather events will increase in frequency and intensity, integrating advanced flood risk mapping into planning and design processes is no longer optional—it is essential.
Digital mapping tools enable architects, developers and planners to identify areas susceptible to flooding, assess potential impacts on planned developments and design resilient structures that account for these risks. By leveraging accurate and detailed data, these tools help professionals make informed decisions, ultimately protecting communities and minimising damage.

What Is Flood Risk Mapping?
Flood risk mapping involves the analysis of geographical and hydrological data to identify areas vulnerable to flooding. Traditional flood maps relied on historical flood records and basic topographic data but modern digital mapping integrates advanced technologies such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), satellite imagery and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). These tools provide a detailed and dynamic understanding of flood risks by accounting for factors such as:
-
Topography: Elevation data helps determine how water flows across the land.
-
Hydrology: Analysing river networks, rainfall patterns and drainage systems highlights areas prone to flooding.
-
Land Use: Urbanisation, deforestation and agricultural practices can exacerbate flooding by altering natural drainage systems.
-
Climate Projections: Incorporating future climate scenarios ensures planning is forward-thinking and adaptable.
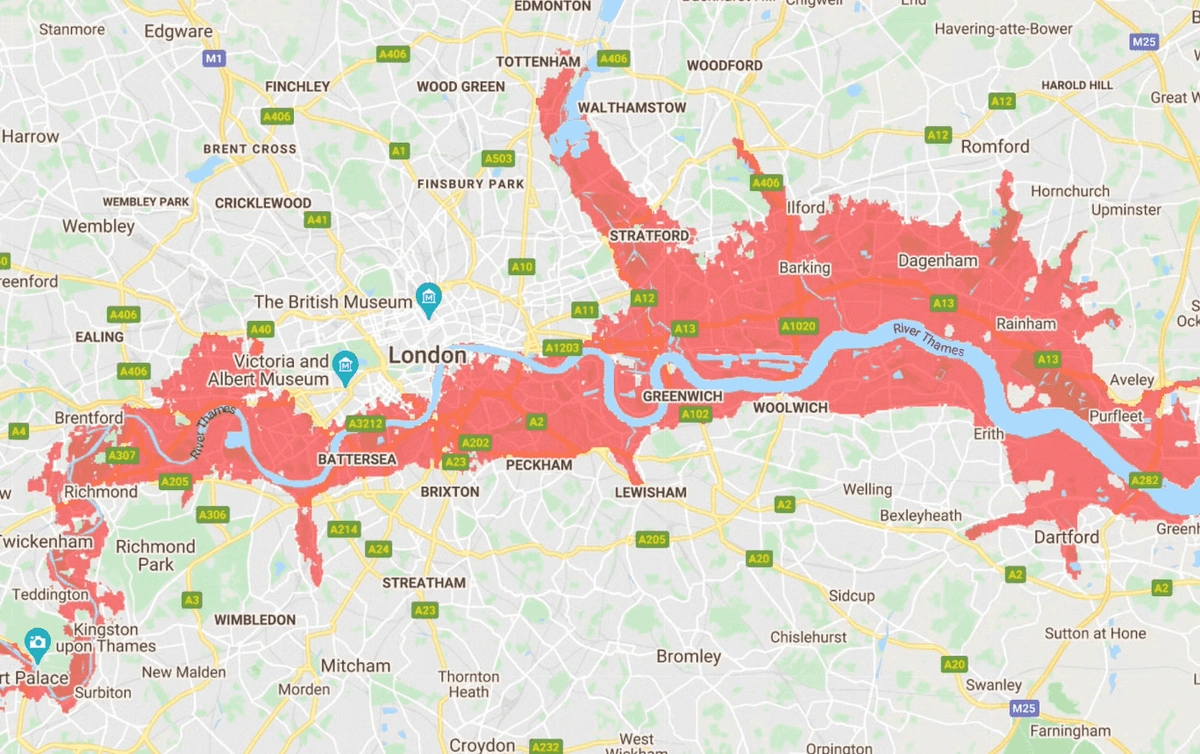
The areas in red face frequent flooding by 2030 (image by NASA)
The Role of Digital Mapping in Flood Prevention
Digital mapping has transformed the way the building industry approaches flood risk management. The following applications highlight how these tools contribute to mitigating flood risks:
1. Site Analysis and Selection
For architects and developers, understanding the flood risk of a potential building site is critical. Digital mapping tools like LiDAR-based contour maps and flood risk datasets provide highly detailed elevation data, allowing professionals to assess whether a site is vulnerable to flooding. In the UK, services such as MapServe offer 1m contour maps that help architects evaluate terrain features and make informed site selection decisions.
In addition to identifying flood-prone areas, these tools enable developers to anticipate challenges related to drainage, access and construction feasibility. Early identification of potential issues saves time and resources during the planning process and ensures projects are both safe and sustainable.
MapServe®’s 1m contour maps provide highly accurate elevation data, enabling architects and planners to assess flood risks with precision. These maps are available for instant download and are compatible with CAD tools for seamless integration.
2. Designing Flood-Resilient Structures
Incorporating flood risk data into the design process ensures that buildings are equipped to withstand flooding. Architects can use digital mapping to determine appropriate elevation levels for structures, identify areas where flood defences are needed and plan for effective drainage systems. For example, raised foundations, permeable surfaces and water-resistant materials are design strategies that can be implemented based on flood risk maps.
Furthermore, flood-resilient design includes integrating features like water barriers, elevated utilities and green spaces that absorb excess water. These measures not only protect the structure but also contribute to the overall resilience of the community.
3. Urban Planning and Drainage Systems
Planners can use digital mapping to design cities that manage water more effectively. By analysing flood risk data, planners can identify areas where sustainable drainage systems (SuDS) are needed to reduce surface water flooding. SuDS solutions, such as green roofs, rain gardens and permeable pavements, can significantly reduce flood risks in urban environments. Digital mapping ensures these systems are placed where they will have the greatest impact.
Additionally, integrating flood risk mapping into urban planning enables local authorities to create zoning regulations that restrict development in high-risk areas. This proactive approach reduces long-term vulnerabilities and ensures future developments are built with resilience in mind.
4. Emergency Response Planning
In the event of severe flooding, digital mapping plays a crucial role in emergency response. Real-time data integration with GIS platforms allows local authorities and emergency services to identify affected areas quickly, plan evacuation routes and allocate resources effectively. This capability is particularly important in the UK where densely populated areas near rivers and coasts are highly vulnerable.
Emergency response plans can also be enhanced by using digital mapping to simulate flood scenarios. These simulations help identify potential bottlenecks in evacuation plans and ensure resources are distributed efficiently to minimise damage and loss of life.
Recent Developments and News in the UK
The UK government has recognised the importance of addressing climate-related flood risks and has taken steps to improve resilience. In 2021, the Environment Agency launched a new Flood and Coastal Erosion Risk Management Strategy, aiming to make the country more resilient to flooding and coastal erosion by 2050. The strategy emphasises the role of innovation and technology in mitigating flood risks, including the adoption of digital mapping tools.
Additionally, in 2022, the Met Office and the Environment Agency enhanced their flood forecasting capabilities by integrating advanced digital technologies. These developments underline the critical role of mapping solutions in addressing climate change challenges.
In the last couple of years, recent events, such as the flooding in South Yorkshire and the Somerset Levels, have highlighted the need for proactive flood risk management. These incidents serve as a reminder of the devastating impact flooding can have on communities and the importance of adopting advanced tools to mitigate these risks.
Somerset Levels
Benefits of Digital Mapping for the Building Industry
The adoption of digital mapping technologies offers several benefits for architects, planners and the wider building industry:
-
Improved Accuracy: High-resolution data ensures precise analysis of flood risks, reducing the likelihood of costly errors in planning and design.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Identifying flood risks early in the planning process helps avoid expensive retrofits or repairs in the future.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Flood risk assessments are a legal requirement for planning applications in flood-prone areas. Digital mapping ensures compliance with regulations and strengthens applications. MapServe®’s OS Topographical Map ensures your planning applications meet regulatory requirements by providing comprehensive land-use data.
-
Sustainability: By integrating flood risk data into designs, professionals can create structures and developments that are more sustainable and resilient to climate change.
-
Enhanced Communication: Detailed flood risk maps facilitate clearer communication between stakeholders, including clients, local authorities and contractors, ensuring everyone has a shared understanding of the risks and solutions.
Choosing the Right Digital Mapping Solutions
Not all digital mapping tools are created equal and choosing the right solution is essential for effective flood risk management. Key considerations include:
-
Data Resolution: High-resolution maps, such as 1m contour maps, provide greater detail for accurate analysis.
-
Ease of Access: Platforms like MapServe® allow users to search, preview and download maps instantly, saving time and effort.
-
Compatibility: Data formats such as DWG and DXF ensure seamless integration with architectural and planning software.
-
Coverage: Ensure the mapping solution provides comprehensive coverage for the areas you are working in.
-
Customisation: The ability to tailor maps to specific project needs can enhance their utility and relevance.

Looking Ahead: Preparing for a Changing Climate
As climate change continues to reshape the UK’s landscape, the building industry must adapt to new challenges. Digital mapping offers a powerful tool for addressing flood risks, enabling architects, planners and developers to build resilient communities that withstand the test of time.
By incorporating accurate and detailed flood risk maps into every stage of the planning and design process, professionals can safeguard properties, reduce environmental impacts and protect lives. In an era where the effects of climate change are increasingly felt, the importance of these tools cannot be overstated.
The UK building industry stands at a pivotal moment. By embracing digital mapping technologies, we can take meaningful steps toward mitigating the risks posed by climate change and creating a safer, more sustainable future. With continued investment in innovative tools and collaboration among industry stakeholders, the UK can lead the way in climate-resilient development.