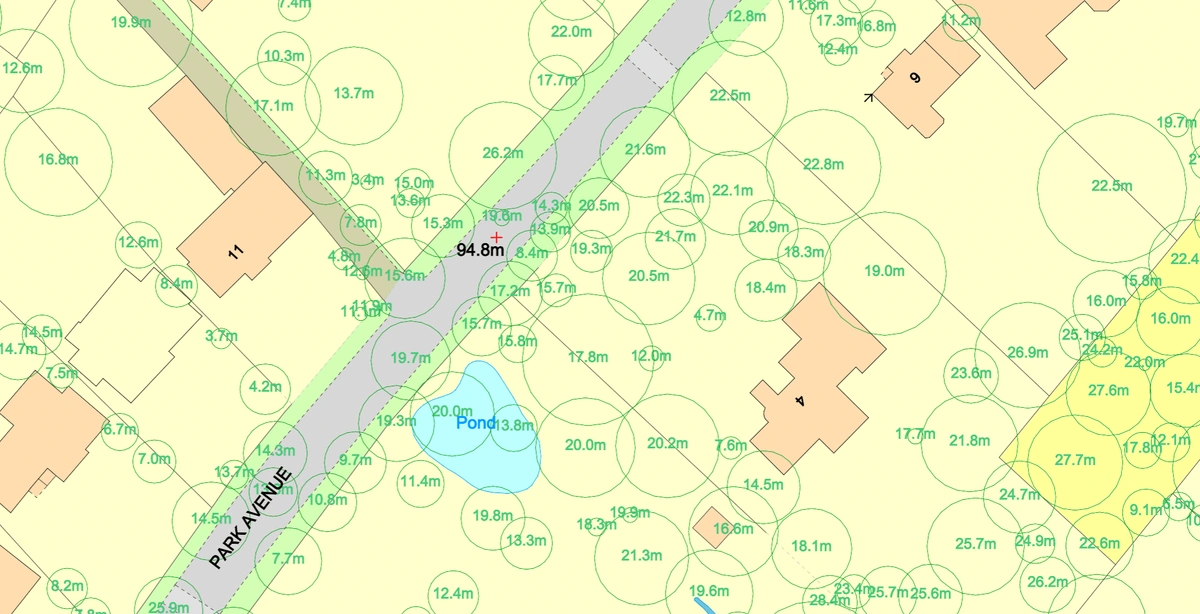
The National Tree Map™ (NTM™) offers a groundbreaking way to understand and manage tree data across the United Kingdom. This high-resolution dataset, created using advanced aerial imagery and LiDAR technologies, provides unparalleled detail about tree canopy coverage, height, and location. As environmental concerns grow, and policies around biodiversity and urban greening become more stringent, the NTM™ emerges as an essential tool for planning, research, and sustainable development. It goes far beyond simple mapping—helping to shape strategies for carbon capture, urban health, and climate resilience. This blog explores the transformative power of NTM™ data, illustrating its diverse applications and highlighting opportunities to leverage its potential across various markets.
What is the National Tree Map™?
The National Tree Map™ (NTM™), developed by Bluesky International, is an extensive dataset containing detailed information about tree canopy coverage, height, and location across the UK. This data is derived from aerial imagery, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data, and other advanced remote sensing technologies. Unlike generic land cover datasets, the NTM™ provides high-resolution data that captures individual trees, making it an invaluable resource for multiple industries.
Download the National Tree Map™ here
Applications of NTM™ Data
The uses of NTM™ data extend far beyond simple mapping. Below are some of its key applications across different sectors:
1. Urban Planning and Development
NTM™ data helps urban planners design green infrastructure that improves quality of life in cities. By analysing tree canopy coverage, planners can identify areas that require additional greenery to mitigate urban heat islands, enhance air quality, and provide recreational spaces. Additionally, NTM™ data supports developers in meeting biodiversity net gain (BNG) legislation by incorporating tree planting into new housing projects.
2. Risk Management
Understanding tree locations and heights is crucial for managing risks associated with storms and tree falls. NTM™ data helps utility companies manage vegetation near power lines and transport authorities ensure roadside safety. Accurate data also assists local councils in preventing damage to property caused by overgrown or unstable trees.
3. Environmental Modelling
Environmental scientists use NTM™ data for creating models that address climate adaptation and biodiversity loss. For example, tree canopy data is integrated into air quality models to predict the impact of urban greenery on pollution levels. Similarly, carbon capture calculations derived from NTM data quantify the contribution of trees to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Health and Wellbeing
Green spaces are vital for physical and mental health. Public health organisations use NTM™ data to map green space accessibility and correlate it with health outcomes such as respiratory health and heat resilience. For instance, studies on canopy cover and heatwaves have shown that areas with higher tree density experience cooler temperatures, reducing heat-related illnesses.
5. Tree Management and Inspections
Local councils and forestry managers benefit from NTM™ data by efficiently managing their tree inventories. For example, councils use Geographic Information Systems (GIS) integrated with NTM™ data to identify trees requiring inspections based on their age or health. They can also utilise LiDAR-derived height data to prioritise maintenance of taller trees that pose potential risks near public spaces or infrastructure. Additionally, NTM™ data helps plan tree planting initiatives by identifying gaps in canopy coverage across urban areas, ensuring resources are directed to areas of greatest need. Tree inspection processes become more streamlined with precise information about tree locations, heights, and canopy coverage, saving time and resources while ensuring public safety.
6. Carbon Sequestration and Biodiversity Conservation
Carbon capture calculations derived from NTM™ data provide critical insights into how trees contribute to mitigating climate change. Environmental consultancies use this data for habitat assessments and biodiversity restoration projects, ensuring compliance with ecological regulations.
7. 3D Visualisations and Modelling
NTM™ data can be used to create 3D models of trees and landscapes. These models are applied in real-world scenarios such as urban visualisation, where architects and city planners simulate how proposed developments interact with existing green spaces. They are also invaluable in disaster planning, enabling authorities to predict and mitigate risks such as tree falls during storms or the impact of deforestation on flood-prone areas. By integrating 3D modelling with additional datasets, stakeholders can make informed, proactive decisions that enhance urban resilience. These visualisations are particularly useful for urban designers and architects to assess how new developments interact with existing green infrastructure. Contour and spot height data further enhance these models by helping identify suitable tree species for specific terrains.
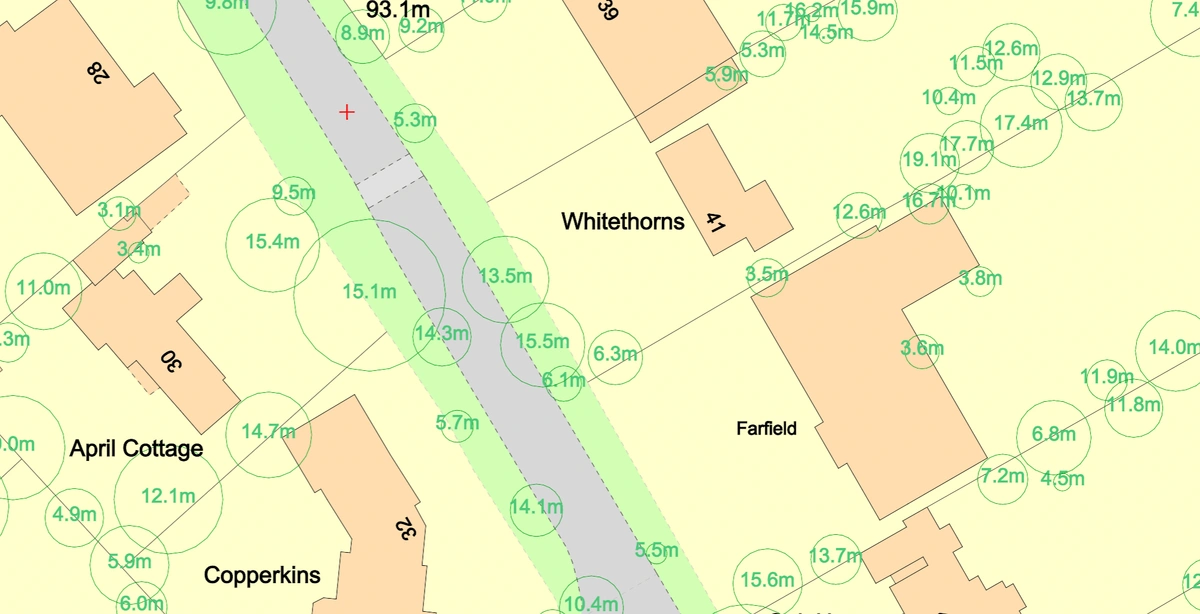
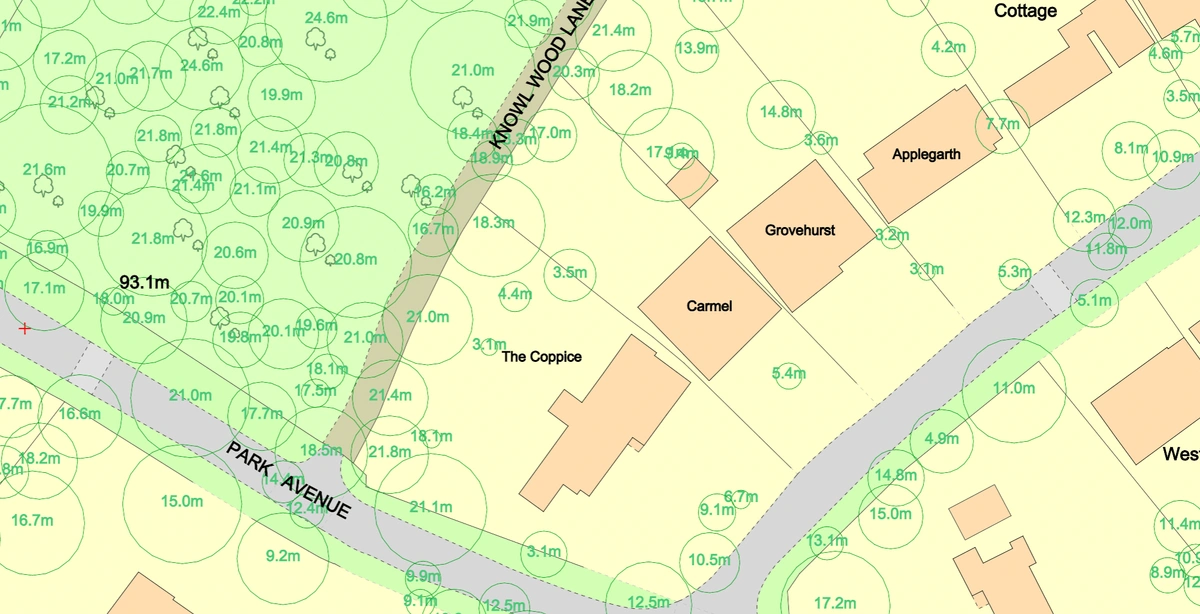
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Quantifying Canopy Cover for Planning and Regeneration
Local councils have used NTM™ data to quantify tree canopy coverage in planning applications. For example, a site with 22% tree canopy coverage may require additional planting to meet environmental standards. This data allows planning departments to set conditions for increasing canopy cover, ensuring that urban developments align with sustainability goals.
Supporting Tree Planting Funding Bids
NTM™ data has been instrumental in securing funding for tree planting in deprived areas. By combining tree canopy data with census information on deprivation, organisations can provide compelling evidence to support funding bids for projects like Greencare’s urban reforestation initiatives.
Public Health Studies
In one health study, NTM™ data was overlaid with heatwave-related mortality rates and respiratory health datasets. This helped public health teams identify high-risk areas and implement targeted interventions, such as planting trees to mitigate urban heat islands and improve air quality.
Environmental Consultancy
The Environment Partnership (TEP) used NTM™ and National Habitat Map (NHM) data for desktop analyses of carbon sequestration, ecological assessments, and compliance with biodiversity net gain (BNG) legislation. This highlights how NTM™ data fills a critical gap in environmental consultancy markets.
Potential Markets for NTM™ Data
The versatility of NTM™ data makes it relevant to a wide range of sectors. Below are key markets and stakeholders that can benefit from this resource:
1. Local Governments and Planning Authorities
Local councils and planning authorities can use NTM™ data for urban planning, environmental modelling, and enforcing regulations such as Tree Preservation Orders (TPOs). It also supports policy-making around green infrastructure and climate resilience.
2. Environmental Consultancies
Organisations like TEP leverage NTM™ data for carbon sequestration assessments, biodiversity restoration, and ecological surveys. This data enhances their ability to provide actionable insights to clients.
3. Utility and Infrastructure Companies
Utility companies can manage vegetation near power lines to prevent outages, while transport authorities can mitigate risks from overgrown trees along roads and railways.
4. Real Estate and Developers
Developers can incorporate NTM™ data into housing projects to meet BNG requirements and enhance property value. Tree canopy coverage is increasingly seen as a desirable feature in real estate.
5. NGOs and Environmental Organisations
Non-profits working on reforestation and biodiversity projects can use NTM™ data to plan and monitor their initiatives. For example, combining canopy data with census information allows organisations to target tree planting efforts in deprived areas.
6. Public Health Organisations
Public health bodies can use NTM™ data to study the relationship between green spaces and health outcomes. This data supports initiatives aimed at improving urban health and reducing heat-related risks.
7. Academia and Research
Universities and research institutions conducting studies on urban ecology, climate change, and biodiversity rely on high-quality datasets like NTM™ to drive their research forward.
8. Forestry and Agricultural Sectors
Forestry managers can use NTM™ data for tree asset management, while farmers can optimise agroforestry practices to balance productivity and sustainability.
Why NTM™ Data is Useful
-
Accuracy and Detail: High-resolution data capturing individual trees ensures reliable insights.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet legislative requirements such as BNG and environmental impact assessments.
-
Customisation: Data can be tailored to specific needs, whether it’s urban planning, environmental consultancy, or public health.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Saves time and resources by providing ready-to-use data for tree inspections, canopy analysis, and more.
The National Tree Map™ Also make is more than just a dataset; it is a transformative tool that bridges the gap between environmental data and actionable insights. Its applications across urban planning, environmental conservation, public health, and more make it a vital resource in the UK’s journey towards a greener and more sustainable future. For organisations looking to harness the power of data, NTM™ provides an unparalleled opportunity to innovate, comply with regulations, and drive meaningful change. It is offered as an additional layer to OS MasterMap® through MapServe®.
By identifying the right stakeholders—from local councils to environmental consultancies—and highlighting its unique benefits, NTM™ data can unlock significant value in both the public and private sectors. Whether you’re a planner, developer, or environmentalist, the National Tree Map™ is an investment in a greener tomorrow.