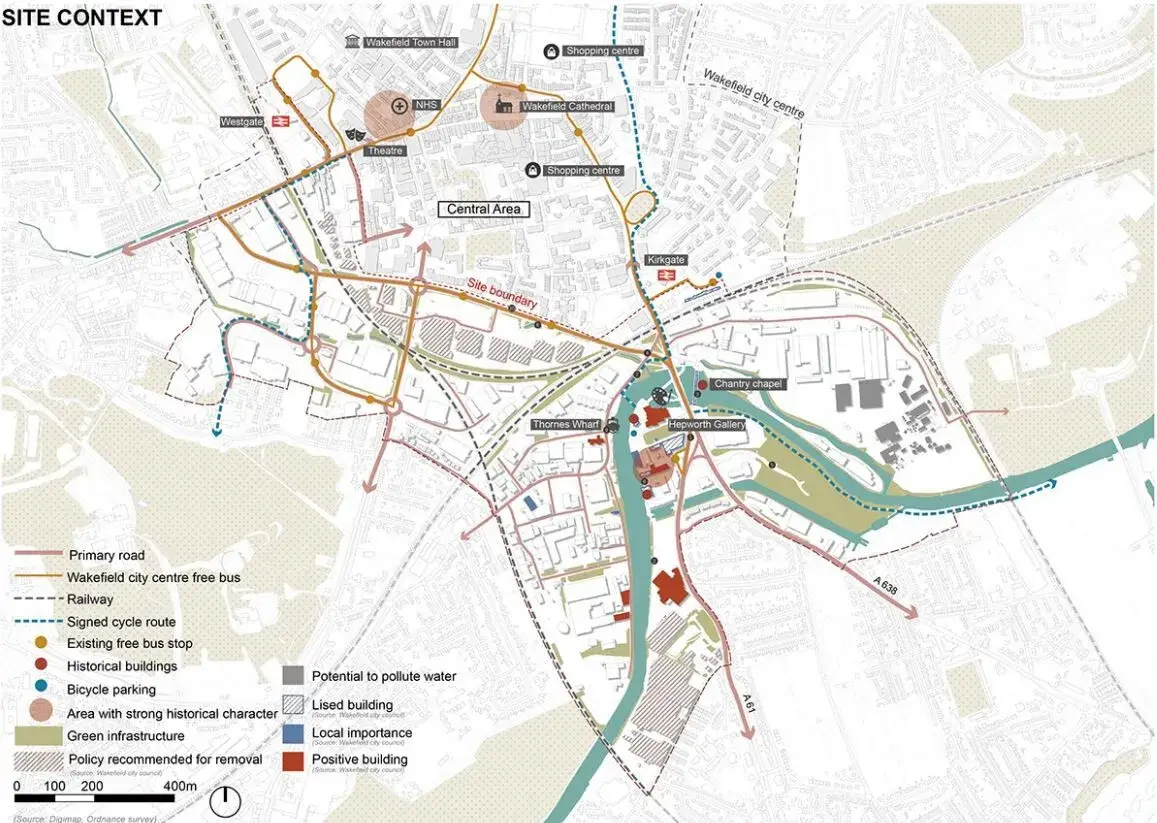
As cities in the UK and around the world continue to grow, the need for smarter, more sustainable urban environments is becoming increasingly urgent. For architects and urban planners, digital maps have become essential tools that offer deep insights into a wide range of factors affecting the built environment. These tools provide accuracy, efficiency, and the ability to analyse complex data, helping professionals make more informed decisions. From the initial stages of site analysis to project execution, digital mapping technology is transforming how we approach urban planning and design.
In this guide, we’ll explore how digital maps are being used in urban planning and architecture and how these tools can enhance project outcomes across the board.
Download the latest digital mapping from the OS
What Are Digital Maps?
Digital maps are virtual representations of geographical areas that are enriched with various layers of data, including topography, infrastructure, environmental factors, and demographic information. Created using Geographic Information Systems (GIS), satellite imagery, and 3D modelling, these maps allow urban planners and architects to visualise the physical space they are working with, helping them to plan and design with greater precision and foresight.
The Role of Digital Maps in Urban Planning
1. Site Analysis and Feasibility Studies
Before any development or construction project begins, it's vital to understand the site in detail. Digital maps allow urban planners to conduct thorough site analyses by providing access to comprehensive data, such as land elevation, vegetation, hydrology, and proximity to existing infrastructure.
For instance, when planning a new residential area in a city like Manchester, urban planners can use digital mapping tools to evaluate existing transport links, assess flood risk areas, and determine proximity to local amenities. This data helps in making informed decisions about the feasibility of the site and identifying challenges early in the process. Additionally, planners can use demographic data layers, such as population density and income levels, to tailor the project to the needs of local communities.
2. Optimising Land Use and Planning
In cities like London, where space is at a premium, effective land use is critical. Digital maps provide a visual representation of current land use and planning policies, helping urban planners identify appropriate areas for new development. By layering multiple data points—such as transport networks, environmental constraints, and social infrastructure—planners can ensure that land is used in the most efficient and sustainable way possible.
Take, for example, the London Plan, which serves as a framework for development across the capital. This plan relies on digital mapping technology to guide decisions on where to allocate land for housing, business districts, parks, and industrial areas. By leveraging data from digital maps, planners can make more informed choices about where development should occur, ensuring that it aligns with existing transport and environmental priorities.
3. Environmental Impact Assessment
In the context of the UK’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero targets, digital maps play a crucial role in assessing the environmental impact of urban development projects. These tools enable planners to visualise environmental data such as flood risks, air pollution levels, and biodiversity hotspots.
For example, on projects like the construction of new urban rail systems or motorways, digital maps are used to assess the environmental implications. GIS technology allows planners to avoid ecologically sensitive areas and design mitigation strategies, such as green corridors or buffer zones, to minimise environmental harm.
4. Transportation and Mobility Planning
Effective transport infrastructure is fundamental to the success of any urban development. Digital maps allow planners to model transport systems, analyse traffic patterns, and optimise public transport networks. By simulating multiple scenarios, planners can identify solutions that reduce traffic congestion, improve public transport efficiency, and promote greener modes of transport, such as cycling and walking.
In the case of Birmingham’s ongoing development, digital maps have been used to model transport strategies for the city’s future growth. By analysing data on current traffic flows, bus routes, and pedestrian areas, planners can identify areas where new infrastructure is needed and optimise existing networks to improve overall mobility.
5. Community Engagement and Public Participation
Urban planning in the UK is increasingly focused on involving the community in decision-making processes. Digital maps offer an interactive way for planners to engage with the public, making planning proposals more accessible. By providing online platforms where residents can view proposed developments, leave feedback, and even suggest alternatives, digital maps foster transparency and collaboration.
For example, local councils across the UK use GIS platforms to share plans for urban regeneration projects with the public. These interactive maps allow residents to view detailed site plans and give their input on proposed designs, creating a dialogue between planners and communities that helps shape better, more inclusive urban environments.
Urban Brownfield and waterfront regeneration, provided by Jiayu Zhu
Digital Mapping in Architecture
1. Enhanced Visualisation and Design
For architects, digital maps offer a more complete understanding of a site’s physical context. With GIS and 3D modelling, architects can design buildings that integrate easily with their surroundings, accounting for factors like sunlight exposure, prevailing wind patterns and the slope of the land.
For example, leading architectural firms such as Foster + Partners, incorporate digital mapping tools in its designs to create buildings that respond to their environment. Whether designing a skyscraper in London or a mixed-use development in Manchester, the use of digital maps ensures that the structure is both functional and sustainable.
2. Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Accuracy is vital in architectural design, particularly for large-scale developments. Digital maps provide architects with precise site data that can be directly integrated into architectural design software. This minimises the likelihood of errors and ensures that designs are accurate from the outset.
A prime example of this is the Crossrail project in London, where architects and engineers used digital mapping to create accurate 3D models of the underground tunnels and stations. This allowed for more efficient collaboration between different stakeholders and helped to ensure that the project stayed on time and within budget.
3. Collaboration with Other Stakeholders
Architectural projects typically involve collaboration with urban planners, engineers, environmental consultants, and local authorities. Digital maps serve as a centralised platform where all stakeholders can share data and visualisations, ensuring that everyone is working from the same information.
For example, during the development of King’s Cross in London, architects worked closely with planners and transport engineers, using digital mapping tools to share detailed site plans and designs. This helped to streamline communication, reducing the risk of delays and ensuring that all aspects of the project were aligned.
4. Adapting to Changing Regulations
With building regulations in the UK becoming increasingly stringent, particularly around sustainability and energy efficiency, digital mapping tools help architects ensure compliance. Many platforms now integrate building codes and sustainability certifications like BREEAM, allowing architects to design projects that meet regulatory requirements from the outset.
Digital Mapping for Climate Resilience
With climate change becoming an increasingly pressing issue, digital mapping plays a crucial role in building climate-resilient cities. By integrating climate data, such as flood risks, heat maps, and weather patterns, digital maps help urban planners design cities that are more adaptive to environmental challenges. In the UK, digital mapping tools are being used to assess flood-prone areas, inform the placement of green infrastructure, and develop strategies for reducing urban heat islands, making cities safer and more sustainable in the long term.

Flooded areas, UK
Popular Digital Mapping Tools for Urban Planners and Architects
1. Ordnance Survey (OS) Maps
The Ordnance Survey (OS) is the primary mapping provider in Britain, delivering detailed and highly accurate geographical data. Through official partners like MapServe®, OS offers essential mapping resources for urban planners and architects, enabling precise site analysis and development planning across the UK.
2. ArcGIS
ArcGIS provides advanced tools for spatial analysis and data visualisation, commonly used by local authorities for planning purposes.
3. QGIS
QGIS is a flexible, open-source alternative to ArcGIS, ideal for smaller-scale projects with powerful mapping capabilities.
4. Google Earth
Google Earth allows users to explore satellite imagery and 3D views, offering a simple solution for preliminary site assessments.
5. AutoCAD Civil 3D
AutoCAD Civil 3D integrates mapping data into the design process, supporting detailed infrastructure modelling and terrain visualisation.
The Future of Digital Mapping in Urban Development
As technology continues to advance, the role of digital mapping in urban planning and architecture will only grow. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and real-time data integration are set to further enhance the capabilities of digital mapping tools. For example, AI-powered analysis can help urban planners predict population growth, traffic patterns, and environmental changes, enabling more responsive and adaptive city planning. Additionally, real-time mapping technologies will allow planners to react dynamically to changing conditions, improving city management and sustainability efforts.
Digital maps have revolutionised urban planning and architecture in the UK, offering a range of tools that allow for smarter, more sustainable development. From optimising land use and planning transport systems to assessing environmental impacts and enhancing public engagement, digital maps enable professionals to design better cities.
As urban areas continue to grow and evolve, the role of digital maps will only become more important, ensuring that the UK’s cities remain vibrant, sustainable and liveable for future generations.