Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionising the geospatial industry, enhancing the accuracy, efficiency, and applicability of mapping technologies. By integrating AI into mapping processes, industries such as urban planning, agriculture, and environmental conservation are achieving unprecedented advancements. This blog post explores the technical aspects of AI integration in mapping, supported by specific examples from leading companies in the field and real-world use cases.
Access the latest OS mapping
Provided by aino
The Role of AI in Mapping
AI enhances mapping in several critical ways, including data collection, processing, analysis, and visualisation. Traditional mapping methods, while effective, are often labour-intensive and time-consuming. AI, with its ability to learn from and make decisions based on data, introduces efficiency and precision into the mapping process.
1. Data Collection and Processing:
One of the most significant contributions of AI to mapping is in the realm of data collection and processing. AI algorithms can analyse vast amounts of data from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground-based sensors. Machine learning models, a subset of AI, are particularly adept at recognising patterns and features in these datasets, enabling the automation of map creation.
For example, Google Maps uses AI to process and interpret satellite images to update its maps continuously. The AI can detect changes in road layouts, new buildings, and even temporary road closures. This level of automation ensures that maps are up-to-date and accurate, providing users with reliable navigation and location information.
2. Enhanced Spatial Analysis:
AI's analytical capabilities significantly enhance spatial analysis, a critical component of geospatial intelligence. Through techniques like predictive modelling and clustering, AI can uncover insights that were previously hidden in complex datasets.
In urban planning, AI-driven spatial analysis can predict urban growth patterns, helping city planners make informed decisions about infrastructure development. For instance, by analysing historical data on population growth, traffic patterns, and land use, AI can predict where future growth is likely to occur, enabling planners to allocate resources more effectively.
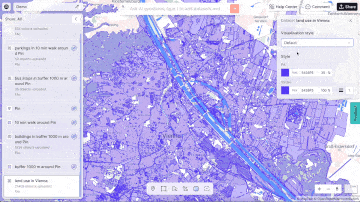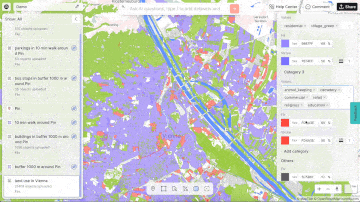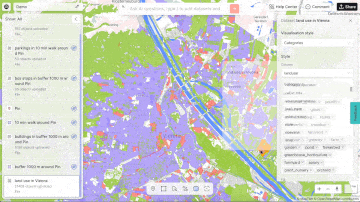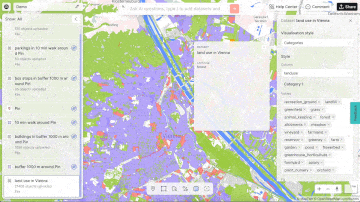
Aino.world, a prominent player in the AI and mapping space, exemplifies this approach. They use AI to analyse urban data, offering solutions that help planners create smarter, more sustainable cities. Their AI models can simulate various scenarios, providing valuable insights into how different planning decisions will impact urban environments.
3. Real-Time Data Integration:
The integration of AI in mapping allows for the real-time updating of maps based on dynamic data inputs. This capability is particularly valuable in applications such as disaster response and traffic management.
In disaster response, AI can process real-time data from social media, weather reports, and emergency services to create dynamic maps that highlight affected areas, safe routes, and resource locations. This real-time information is crucial for coordinating rescue efforts and ensuring timely aid delivery.
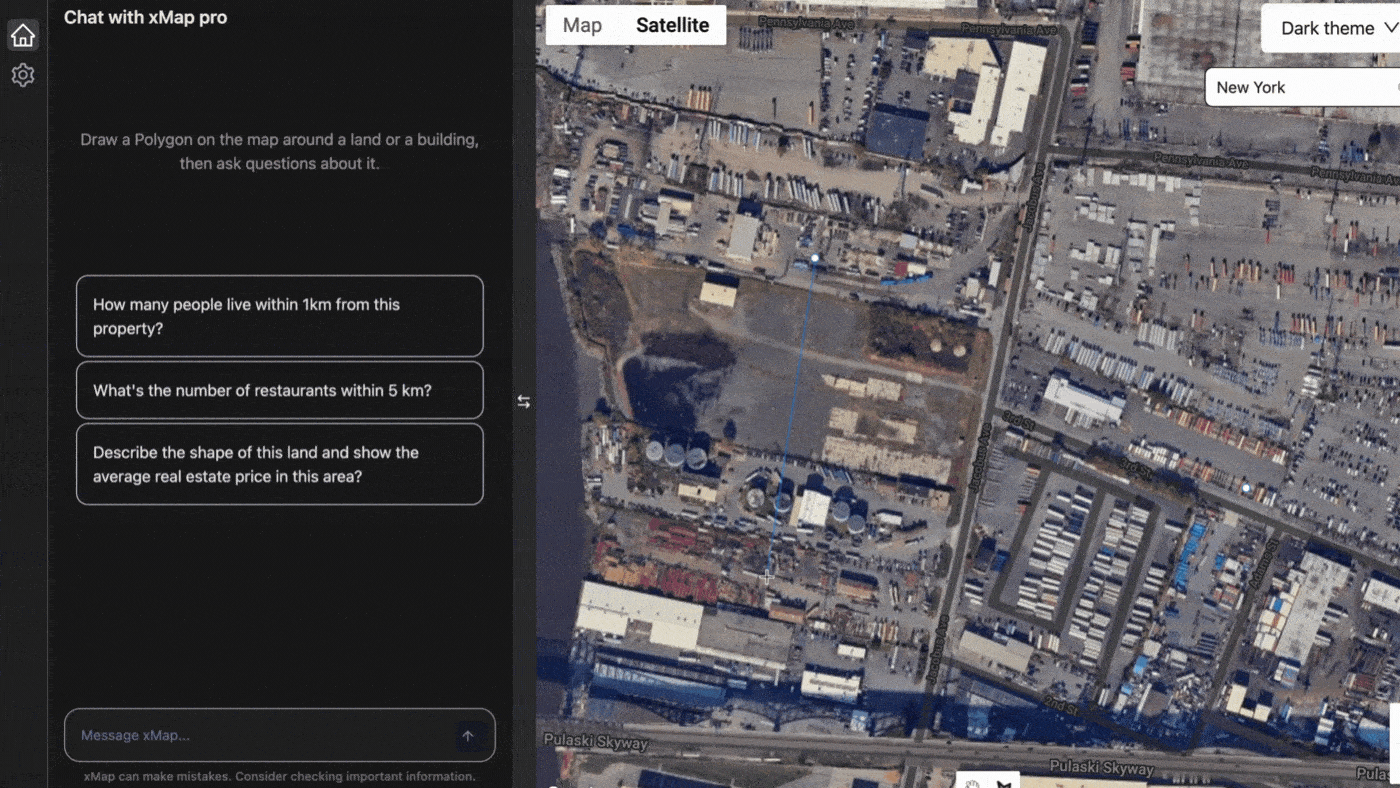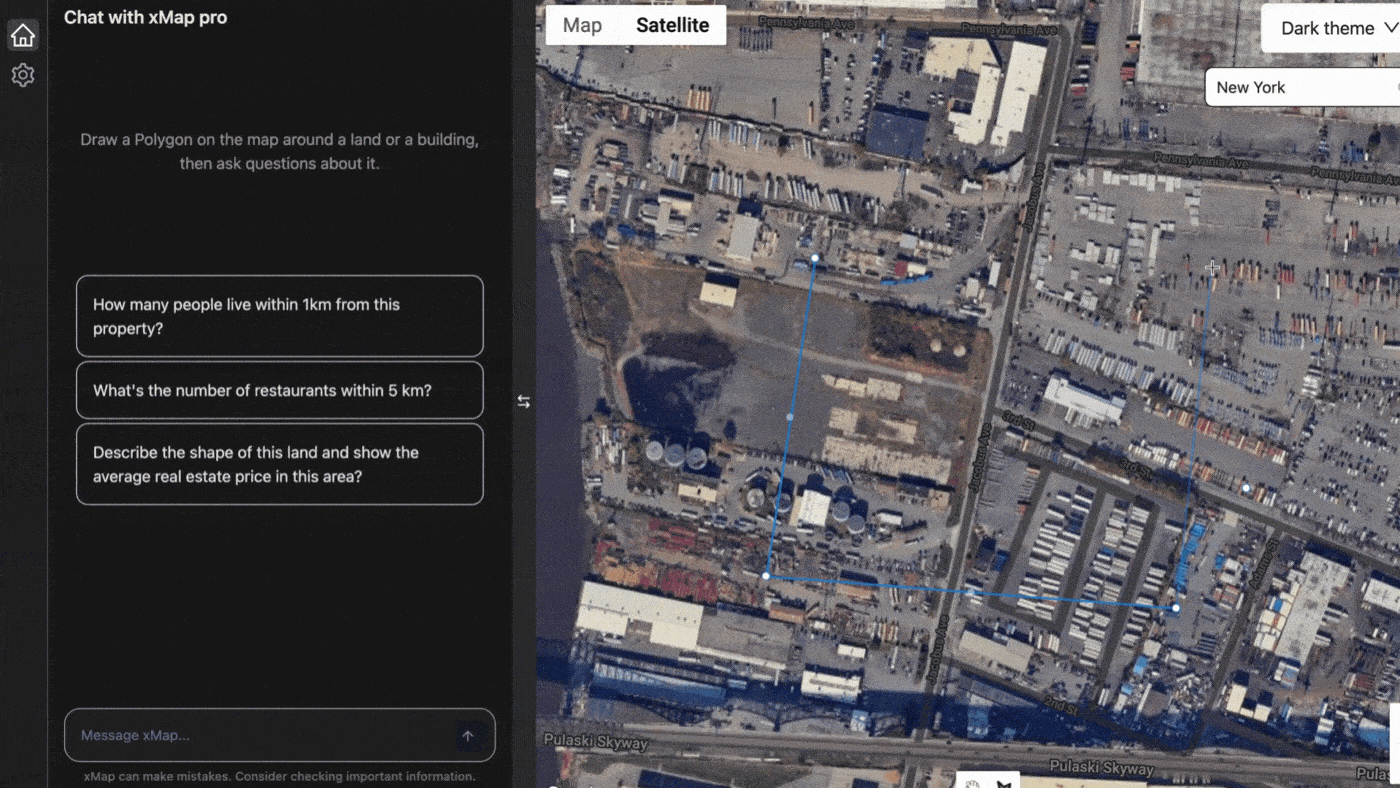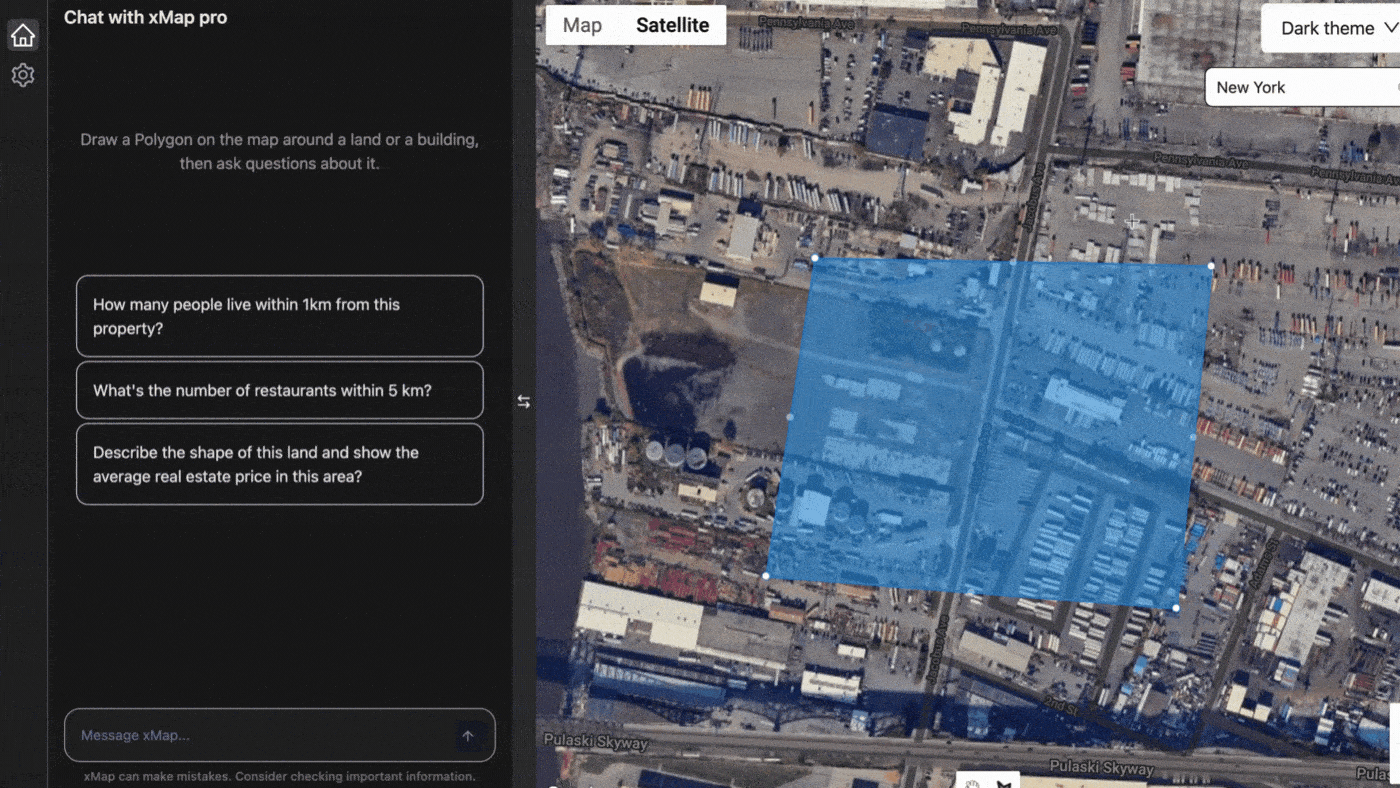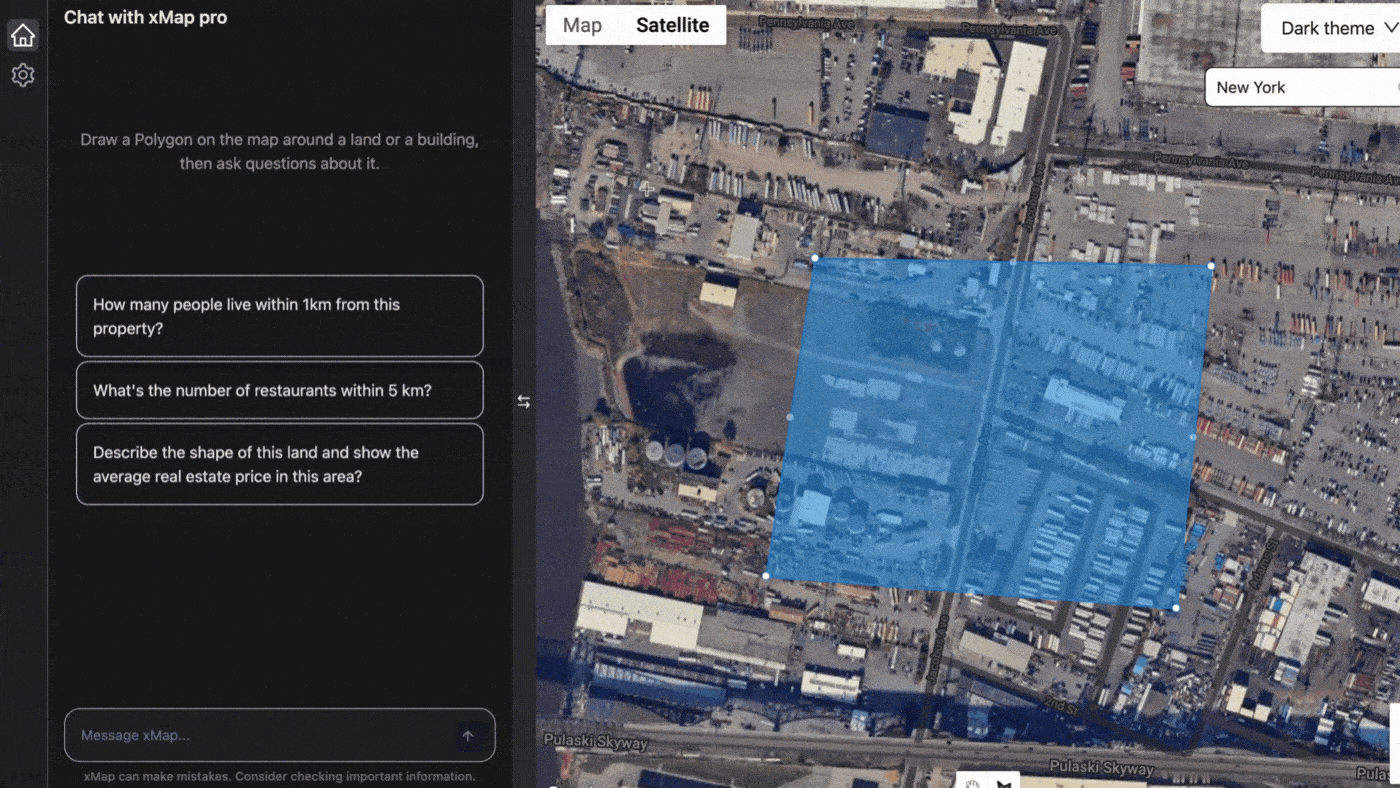
XMap.ai, another leader in the field, leverages AI to integrate real-time data into their mapping solutions. Their platform uses AI to analyse live traffic data, weather conditions, and other variables to provide up-to-date maps for various applications, including emergency response and logistics.
4. Precision Agriculture:
In the agricultural sector, AI integration in mapping has revolutionised precision agriculture. By combining satellite imagery with machine learning algorithms, farmers can gain detailed insights into their fields' conditions.
AI can analyse multispectral images to assess crop health, detect diseases, and monitor soil conditions. This information allows farmers to apply the right amount of water, fertilisers, and pesticides precisely where needed, optimising resources and improving yields.
For example, using AI-powered drones, farmers can capture high-resolution images of their fields. AI algorithms then process these images to provide actionable insights. This technology enables farmers to make data-driven decisions, enhancing productivity and sustainability.
5. Environmental Monitoring and Conservation:
AI integration in mapping is also crucial for environmental monitoring and conservation efforts. AI algorithms can process data from various sources, including satellite imagery and ground-based sensors, to monitor environmental changes and track wildlife.
In conservation, AI can help track animal movements and habitats, identifying patterns and potential threats. This information is vital for developing effective conservation strategies and protecting endangered species.
Additionally, AI can monitor changes in land use, deforestation, and water bodies. By analysing historical and real-time data, AI can detect environmental changes and predict future trends, enabling proactive measures to mitigate adverse effects.
6. Enhanced User Experience:
AI also enhances the user experience in mapping applications. Through natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, AI can provide more intuitive and personalised map interactions.
For instance, AI can improve search functionality by understanding user queries better and providing relevant results. It can also offer personalised recommendations based on user behaviour and preferences, making maps more useful and engaging.
Google Maps, for example, uses AI to provide personalised recommendations for restaurants, attractions, and other points of interest based on users' past behaviour and preferences. This personalisation enhances the overall user experience, making the application more valuable and user-friendly.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
AI-powered mapping solutions are being adopted across various industries, each benefiting from the enhanced capabilities that AI brings.
Urban Planning and Smart Cities: Cities like Singapore and Barcelona are using AI-integrated mapping solutions to manage urban growth and infrastructure. AI helps these cities analyse traffic patterns, optimise public transportation, and plan new developments, ensuring sustainable and efficient urban environments.
Retail and Market Analysis: Retail giants like Walmart and Tesco use AI-driven mapping to analyse consumer behaviour and optimise store locations. By understanding where customers are and predicting future trends, these companies can make data-driven decisions about where to open new stores and how to tailor their offerings to local markets.
Disaster Response and Management: Organisations like the Red Cross and FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) utilise AI-based mapping for disaster response. AI helps them create real-time maps of disaster-affected areas, enabling more effective coordination of rescue efforts and resource allocation.
Environmental Conservation: The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) uses AI-enhanced mapping to monitor wildlife populations and track illegal activities such as poaching and deforestation. AI's ability to process large datasets from satellite images and on-the-ground sensors allows for more effective conservation strategies.
Agriculture: Agricultural companies and research institutions employ AI-driven mapping for precision farming. AI helps farmers monitor crop health, optimise irrigation, and predict harvest yields, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
Transport and Logistics: Companies like DHL and FedEx integrate AI into their mapping systems to optimise delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption, and improve overall efficiency. AI analyses real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and other variables to ensure timely deliveries and cost savings.
Real Estate: Real estate firms leverage AI-powered mapping to identify lucrative investment opportunities. By analysing historical and current data, AI can predict property value trends and help investors make informed decisions.
Telecommunications: Telecom companies use AI-driven maps to plan and optimise network coverage. AI helps them analyse population density, topography, and infrastructure to ensure efficient deployment of communication networks.
Healthcare: In healthcare, AI-integrated mapping aids in epidemiology by tracking disease outbreaks and predicting their spread. Organisations like the World Health Organization (WHO) use these tools to respond swiftly to health crises and allocate resources effectively.
Challenges and Future Directions
While AI integration in mapping offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges. Data privacy and security are significant concerns, as AI systems require access to large amounts of data. Ensuring that this data is collected and used responsibly is crucial. Moreover, the accuracy of AI models depends on the quality of the data they are trained on. Poor quality or biased data can lead to inaccurate results and flawed decision-making. Therefore, maintaining high data quality and addressing biases is essential for effective AI integration.
Looking forward, the future of AI in mapping holds exciting possibilities. Advances in AI technologies, such as deep learning and neural networks, will continue to enhance mapping capabilities. The integration of AI with other emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and augmented reality (AR), will create even more sophisticated and interactive mapping solutions. For example, IoT devices can provide real-time data inputs to AI systems, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of maps. AR, combined with AI, can create immersive and interactive map experiences, revolutionising how we interact with geospatial information.
Provided by xmap
In conclusion, AI integration in mapping is transforming the geospatial industry, offering significant advancements in data collection, processing, analysis, and visualisation. Companies like Aino.world and XMap.ai are at the forefront of this transformation, demonstrating the immense potential of AI-powered mapping solutions. As AI technologies continue to evolve, the future of mapping looks promising, with endless possibilities for innovation and improvement.