When submitting a planning application in the UK, the accuracy of your mapping is paramount. Planning authorities rely heavily on maps to understand the context and specifics of your proposal and any errors can lead to costly delays or outright rejection. This blog will outline the top ten mapping mistakes often seen in planning applications and offer practical advice on how to avoid them.
Download the latest update of OS MasterMap®
1. Incorrect Scale
One of the most common errors in planning application maps is the use of an incorrect scale. UK planning authorities generally require maps to be drawn to specific scales, such as 1:1250 or 1:2500 for location plans and 1:500 or 1:200 for site plans. Using the wrong scale can result in misinterpretation of your proposals, leading to potential rejection.
How to Avoid: Always refer to the specific requirements of your local planning authority (LPA). Ensure that your maps are produced at the correct scale by using professional mapping software or purchasing maps from accredited providers like Ordnance Survey.
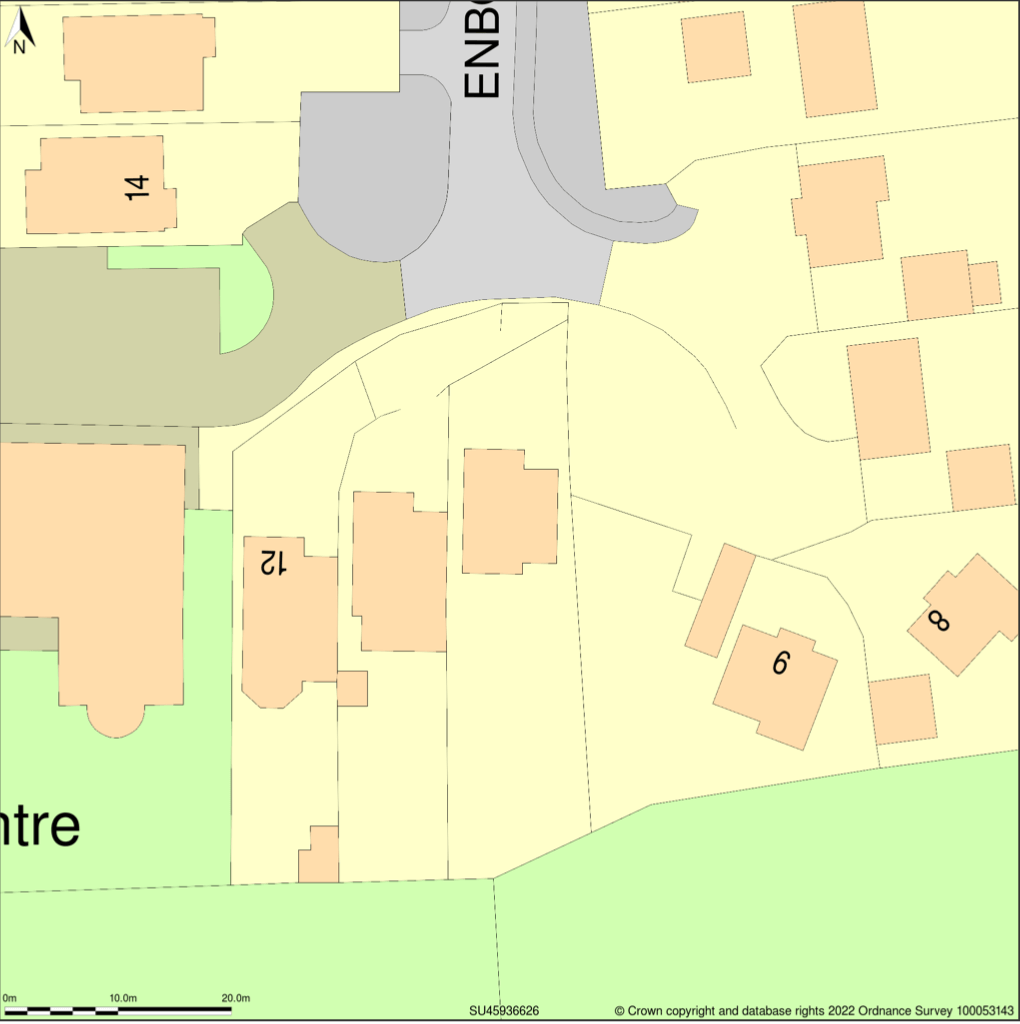
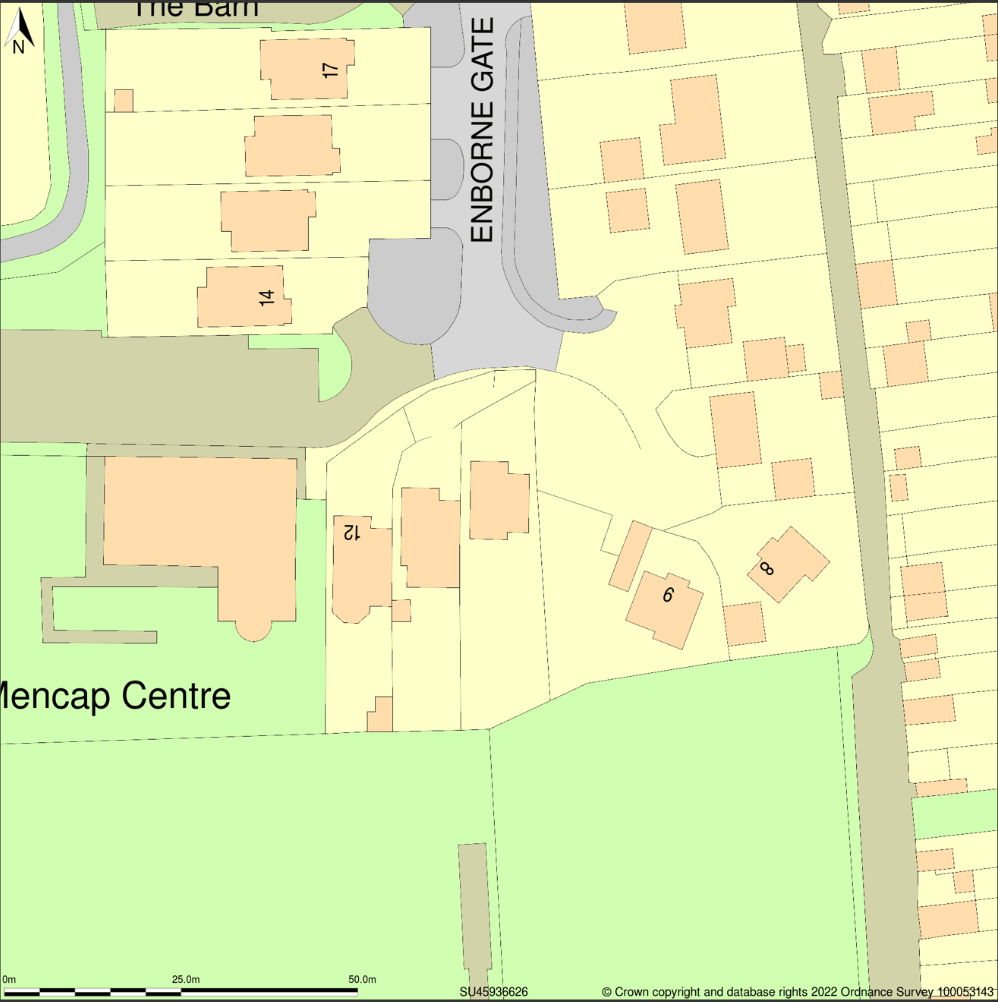
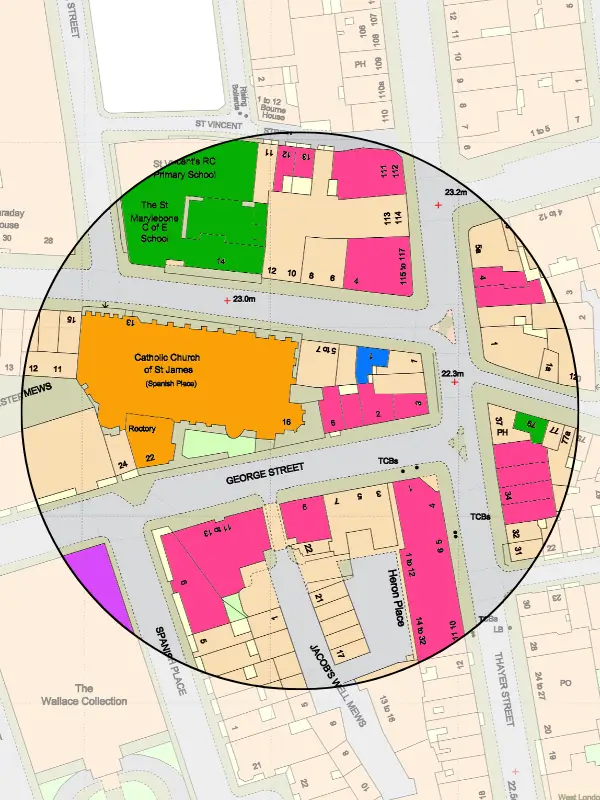
Site Plan at 1:500 scale Location plan at 1:1250 scale
2. Outdated Base Maps
Planning applications should reflect the most current layout of the land and surrounding areas. Using outdated base maps can lead to significant errors, such as failing to show recent developments, new roads, or changes in land use.
How to Avoid: Always obtain the latest version of the map from a reliable source. For example, on MapServe® we always offer the latest update of OS MasterMap®, sourced from Ordnance Survey, ensuring that your planning application reflects the most accurate and current data available. MasterMap® gets an update every 6 weeks and you can check the latest update date on the OS website.
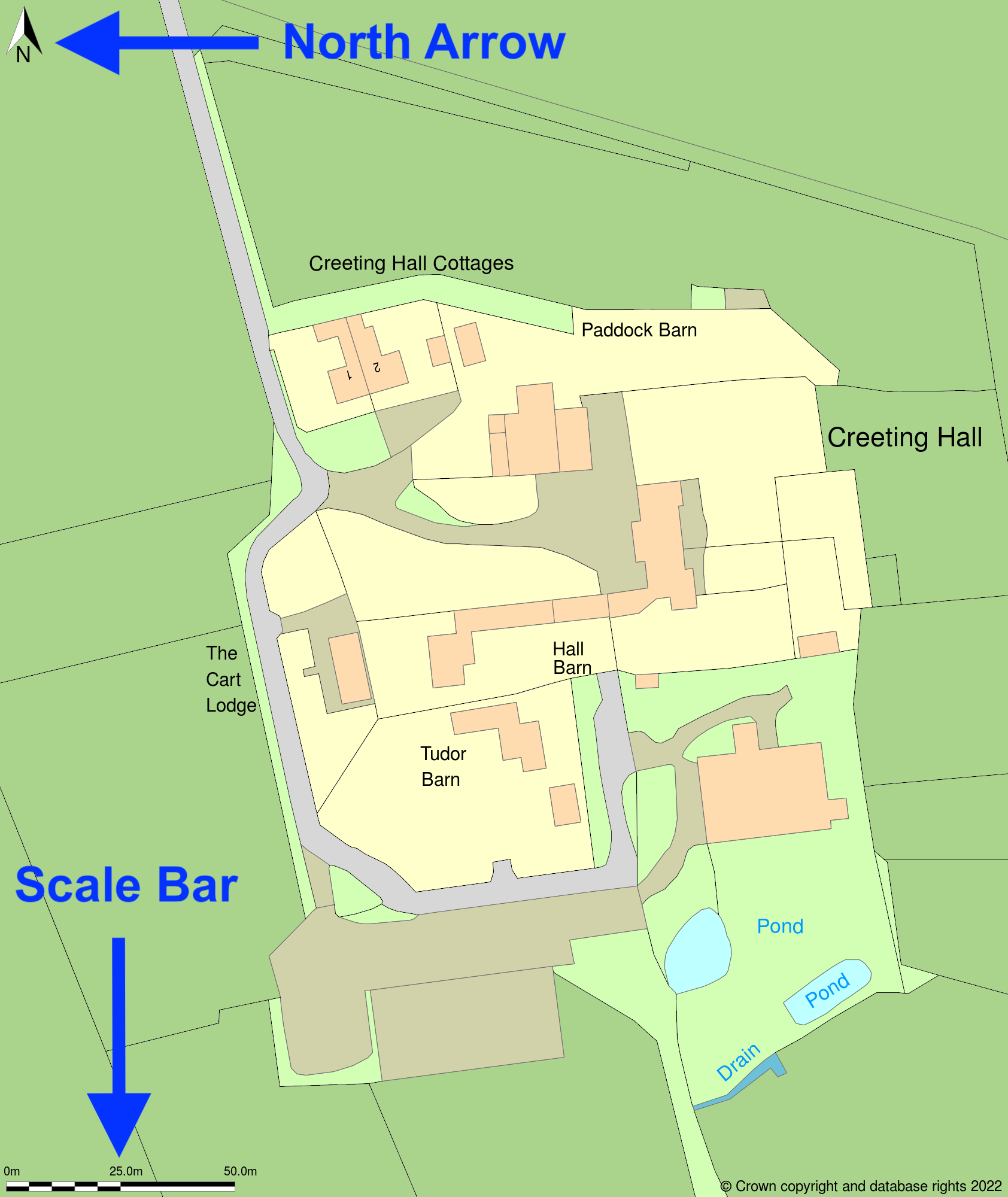
3. Lack of North Arrow and Scale Bar
Maps submitted without a north arrow or scale bar are often rejected because they lack essential orientation and measurement information. These elements are critical for planning officers to accurately assess the proposal's context.
How to Avoid: Always include a north arrow and a scale bar on every map submitted with your planning application. These can typically be added easily using mapping software or by annotating purchased maps.
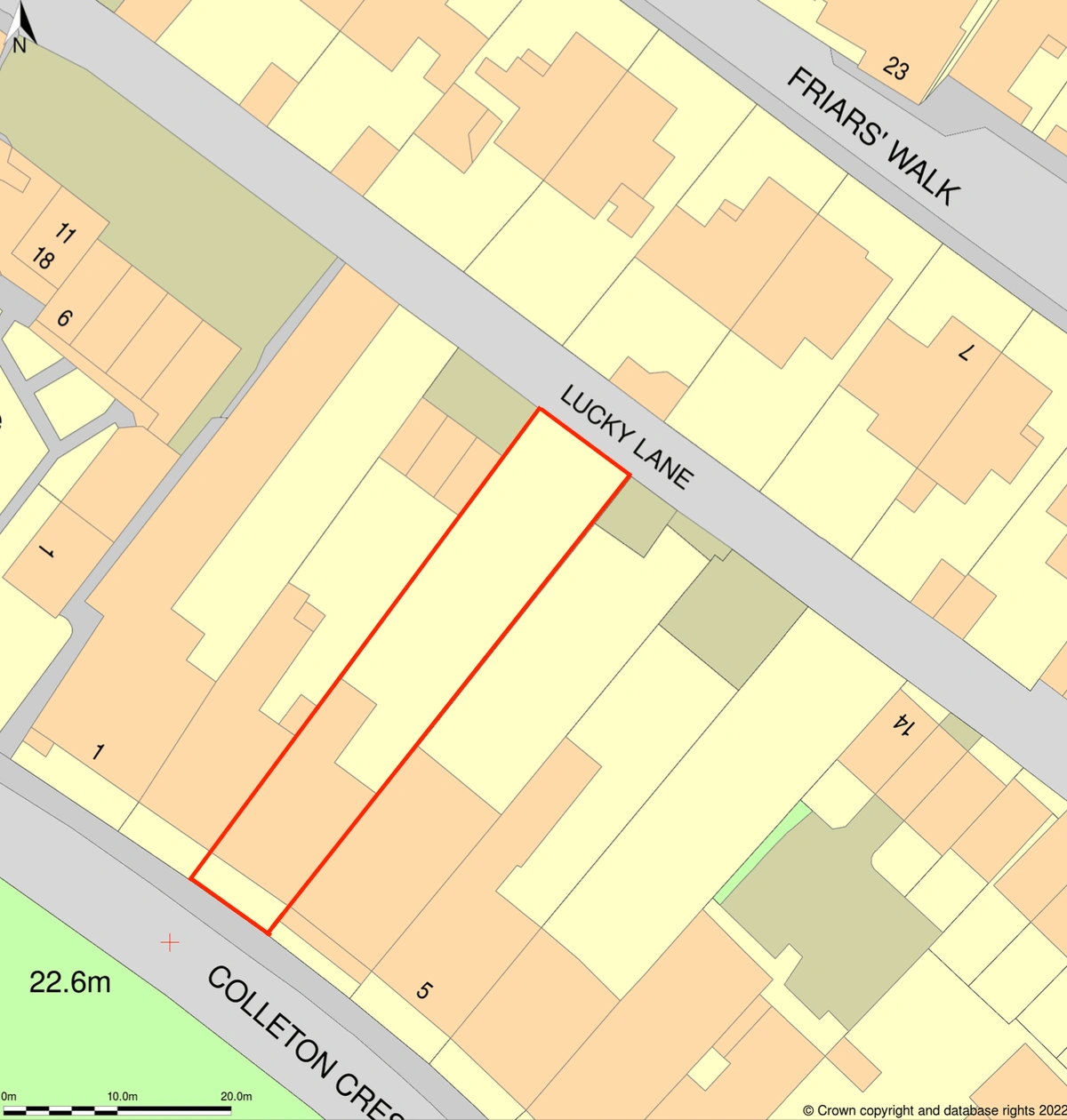
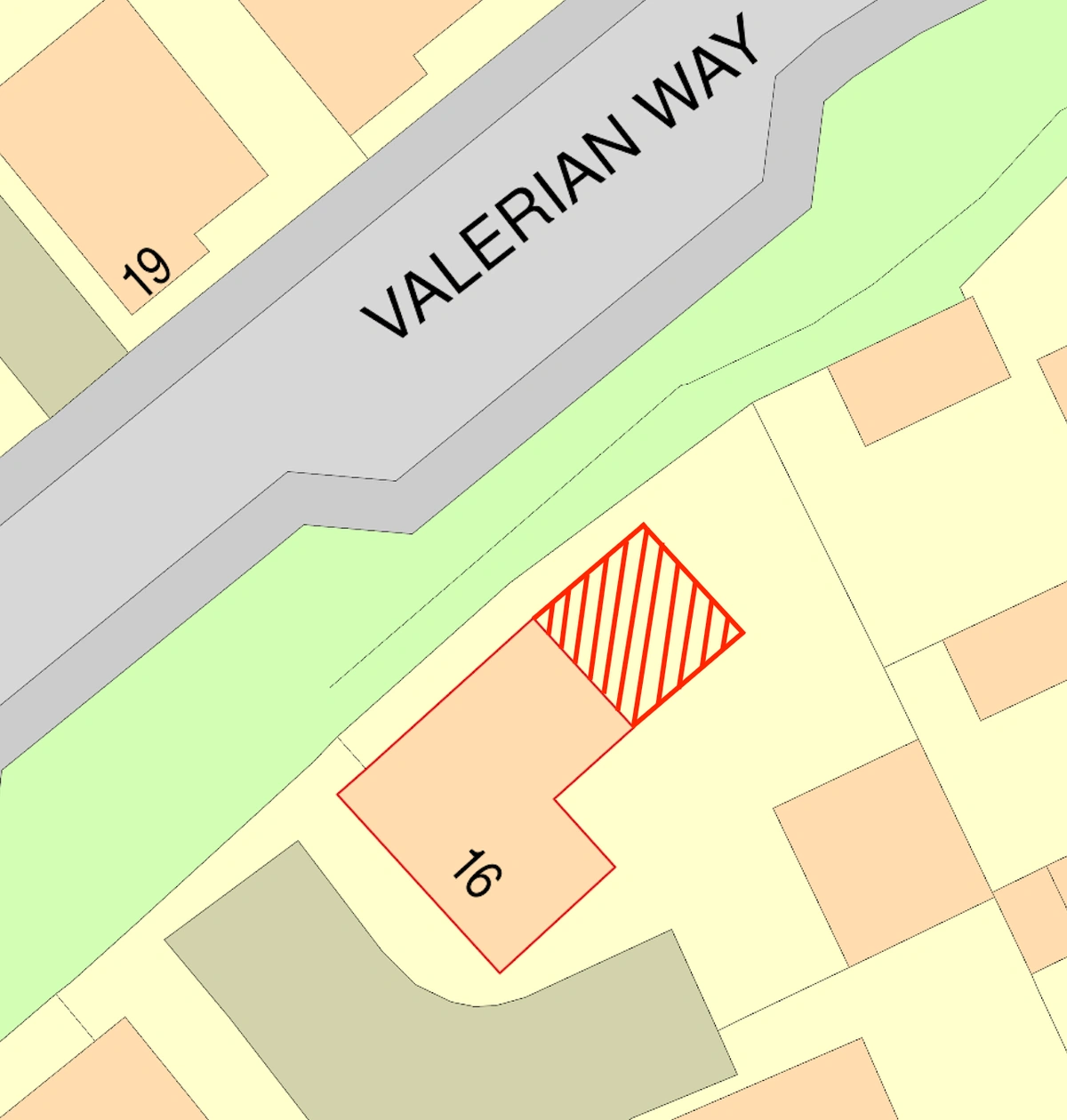
4. Inaccurate Boundaries
Another frequent mistake is the incorrect delineation of property boundaries or the red and blue lines on the location and site plans. An incorrect boundary can lead to disputes, objections from neighbours, or confusion during the planning review.
How to Avoid: Carefully check property boundaries using the most recent title deeds or land registry documents. If in doubt, consult with a professional surveyor to ensure accuracy. Make sure the red line encompasses all the land necessary for the development, including access routes and the blue line covers other land owned by the applicant. Our platform also allows you to draw and adjust boundaries with precision, reducing the risk of errors using one of our drawing tools available. MapServe® provides various tools to help outline the boundaries.
5. Omission of Key Features
Failing to show key features such as trees, hedgerows, watercourses, or existing structures can significantly impact the assessment of your application. These omissions can result in further information being requested or the application being refused.
How to Avoid: Ensure that all relevant natural and man-made features are included on the map. If trees or other landscape features are present, consider commissioning an arboricultural survey and include the findings on your plans. Double-check the local authority's requirements for additional features that need to be shown. The National Tree Map™ can also help as it provides the location, height and canopy extends of trees above 3m.
6. Using Unofficial or Low-Quality Maps
Submitting maps that are not sourced from an accredited provider or that are of low quality (e.g., blurry, pixelated, or incomplete) can lead to your application being rejected outright.
How to Avoid: Always use high-quality, official maps from reputable providers like Ordnance Survey. These maps should be clear, precise, and properly formatted according to the LPA's guidelines. MapServe® is an official supplier of OS mapping and our license number is 100053143.
7. Failure to Show All Relevant Land Uses
Your map needs to accurately represent not only your site but also the surrounding land uses. Failing to show adjacent land uses, such as residential areas, commercial zones, or agricultural land, can lead to an incomplete assessment by the planning authority.
How to Avoid: Conduct a thorough survey of the surrounding area and ensure that your maps reflect the current land use. This is particularly important if your development might impact neighbouring properties or if your proposal includes a change of use. MapServe®'s building use layer can help identify the use of each property.
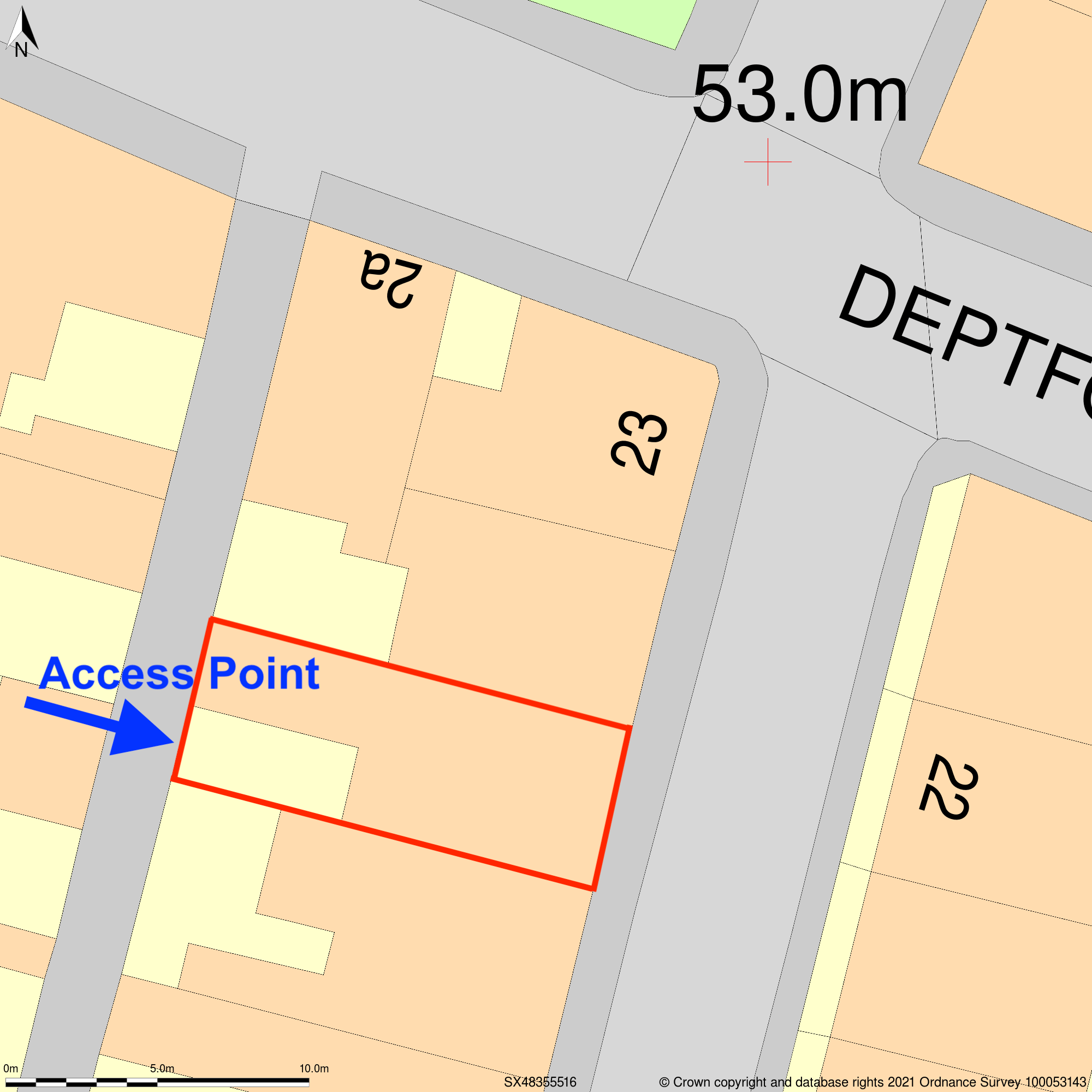
8. Inadequate Site Access Information
One critical aspect often overlooked in planning application maps is the depiction of site access points. Failure to clearly show access routes can lead to objections from highways authorities or neighbours and may result in a request for additional information or amendments.
How to Avoid: Clearly delineate all access points to the site on your block plan, including vehicular, pedestrian and emergency access routes. Ensure these routes meet local highways standards and are clearly marked on the map.
9. Not Showing Existing and Proposed Structures
It's crucial to differentiate between existing and proposed structures on your map. Failure to do so can lead to confusion and might cause the planning officer to misinterpret the scale or scope of your project.
How to Avoid: Use different line types, colours, or shading to distinguish between existing and proposed structures on your site plan. Clearly label each structure to avoid any ambiguity.
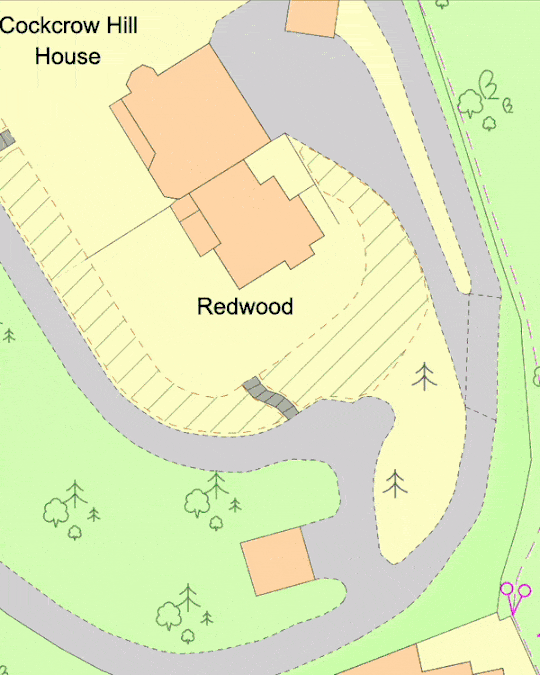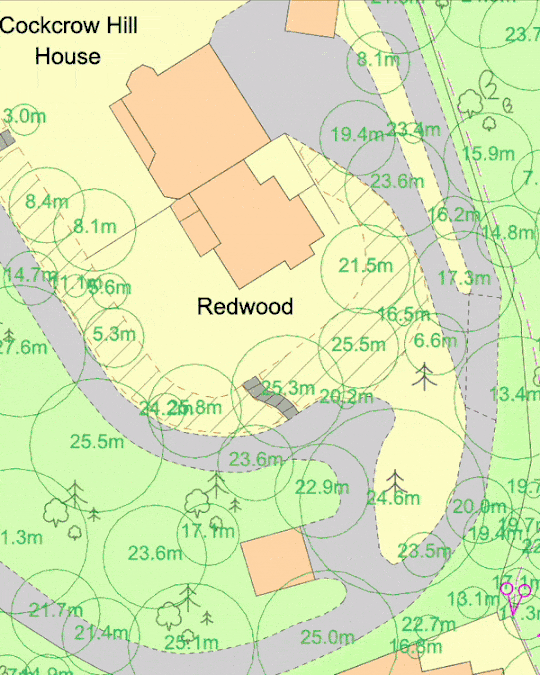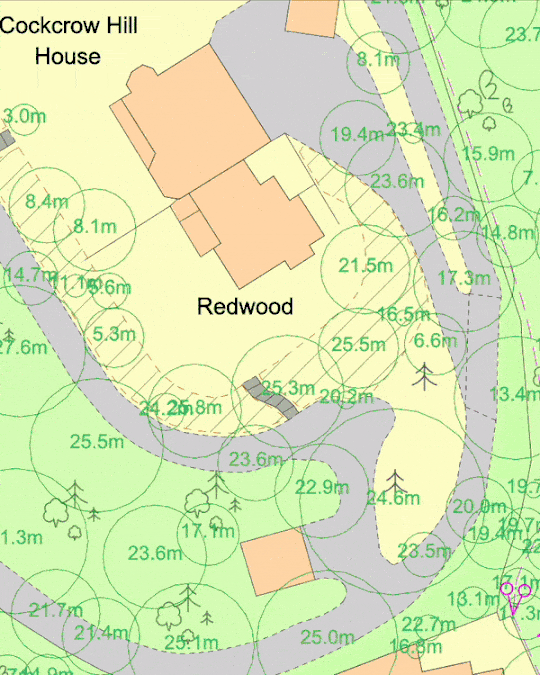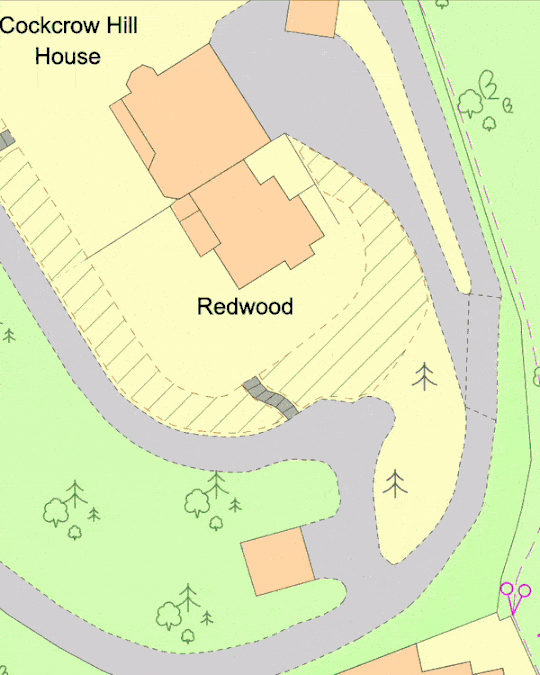
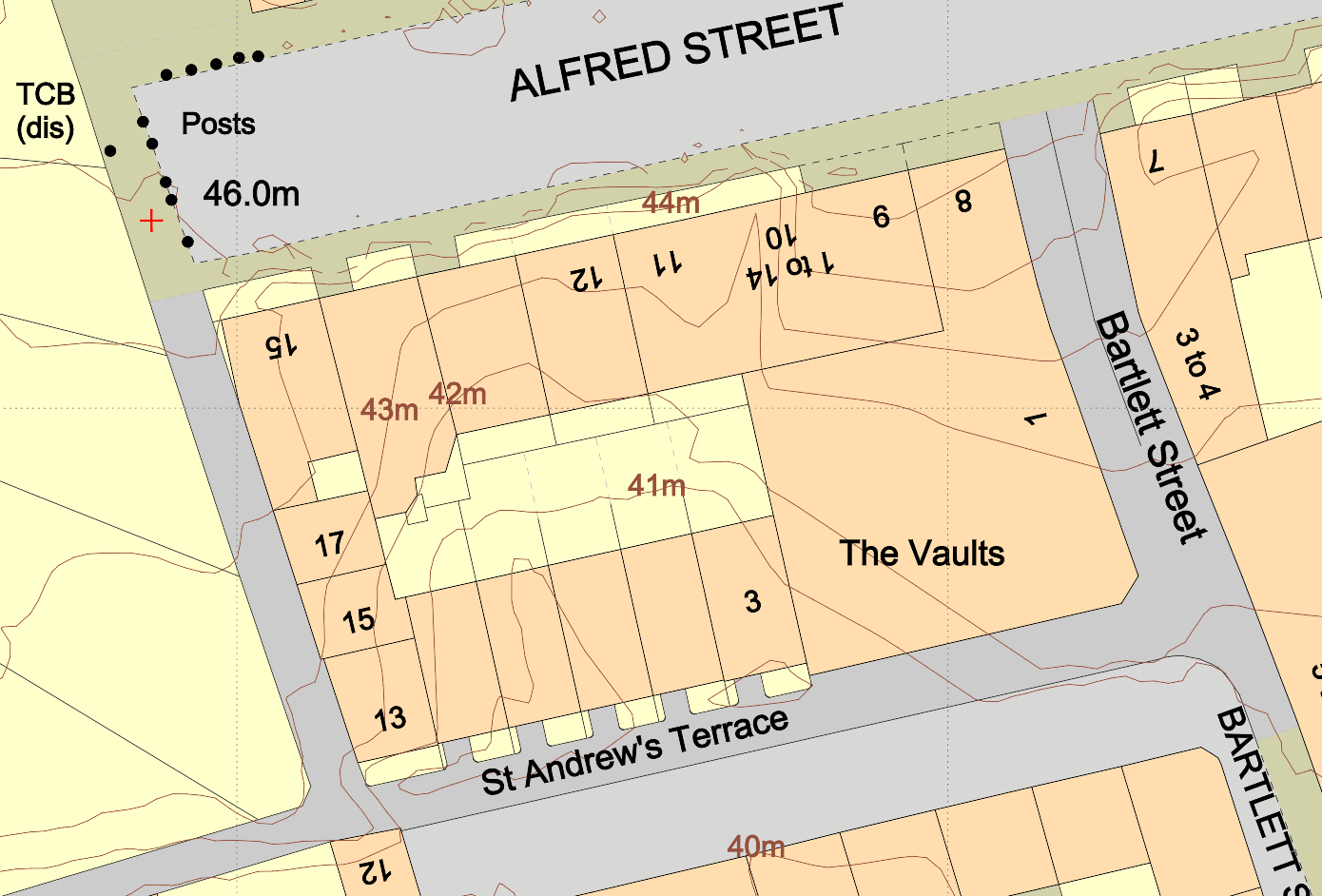
10. Ignoring Topographical Information
Topography can significantly influence the feasibility of a development, especially in areas prone to flooding or where there are significant elevation changes. Neglecting to include topographical information can lead to serious issues during the planning process.
How to Avoid: If your site has significant elevation changes, consider commissioning a topographical survey or adding contours to your mapping. Include contour lines, spot heights, or other relevant information on your site plan to show how the development interacts with the terrain. MapServe® offers 1m contours as an additional layer to OS MasterMap®.
Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance
Avoiding these common mapping mistakes is crucial for the smooth progression of your planning application. By ensuring your maps are accurate, up-to-date, and compliant with local authority requirements, you increase the likelihood of a positive outcome.
Engaging with professionals, whether they be surveyors, architects, or mapping specialists, can provide valuable expertise and ensure that your application is supported by precise and high-quality maps. Additionally, investing in good mapping software or using accredited map providers will help you avoid the pitfalls that lead to rejections and delays.