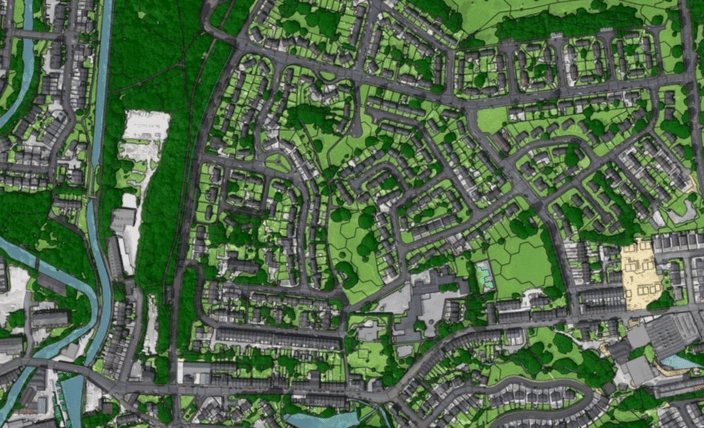
The natural world is under increasing scrutiny as society strives to balance development and conservation. To achieve sustainable progress, precise, reliable, and actionable data about the environment is essential. This is where the Enhanced Land Cover (ELC) Mapping from Ordnance Survey (OS) enters the picture, bringing groundbreaking capabilities to ecologists, developers, and environmental consultants alike.
In this blog, we delve into what makes the ELC mapping unique, its technical strengths, and the transformative impact it is poised to have on a broad range of applications, from biodiversity net gain (BNG) assessments to urban habitat analysis.

What is Enhanced Land Cover Mapping?
At its core, Enhanced Land Cover Mapping is a high-resolution geospatial dataset that provides comprehensive insights into the natural habitats within a defined Area of Interest (AOI). Created with an emphasis on accuracy and usability, this dataset merges authoritative OS data with third-party ecological datasets, offering an unparalleled view of the land and its biodiversity.
The ELC Mapping Minimum Viable Product (MVP) integrates multiple layers of geospatial intelligence derived from:
- 25cm Aerial Imagery: Delivering unprecedented detail of vegetation, habitat structures, and land use.
- OS National Geospatial Database (NGD): Providing context with details on roads, fields, and buildings.
- Third-Party Data: Including ecological datasets like Priority Habitat, Ancient Woodland and other classified natural assets.
By synthesising these data sources, ELC offers actionable intelligence that aids in pre-development planning, natural capital baselining, and ecological conservation efforts.
Download the latest Ordnance Survey Maps
Why Enhanced Land Cover Mapping Stands Out
Ordnance Survey's ELC Mapping sets itself apart through several technical differentiators
1. Unparalleled Granularity
The use of 25cm aerial imagery allows users to capture intricate details of the landscape, surpassing the resolution available through open-source satellite imagery. This granularity ensures that even small ecological features, such as residential gardens in urban settings or subtle vegetation changes, are accurately represented.
2. Integrated Data Ecosystem
The dataset combines trusted OS geospatial data, including imagery and terrain, with established open data sources like Living England and CROME. This reduces the time and expertise needed to reconcile disparate datasets, enabling faster and more effective decision-making.
3. Consistency for Long-Term Monitoring
With consistent data specifications across geographies and time, ELC facilitates comparative studies, allowing landowners and ecologists to monitor change over decades. This is particularly important given the UK’s legislative commitment to BNG monitoring for at least 30 years.
4. Seamless Integration
Delivered in OGC GeoPackage and Esri Shapefile formats, the data integrates effortlessly with most GIS platforms. This approach ensures ecologists and planners can focus on analysis rather than technical obstacles.
5. Provenance and Trust
OS has been the authoritative mapping agency for Great Britain since 1791. Users can trust the accuracy and transparency of the data, which is crucial for regulatory compliance and better decision-making.
Use Cases of ELC Mapping
The versatility of ELC Mapping is reflected in its wide range of use cases. Below are some of the key applications where it can be useful:
1. Biodiversity Net Gain (BNG) Assessments
BNG requirements necessitate developers to leave the environment in a measurably better state post-development. ELC Mapping offers a detailed view of baseline habitats, allowing ecologists to plan restoration or enhancement activities effectively. The integration of third-party condition models further supports precise scoring of habitat quality.
2. Natural Capital Baselines
Understanding the ecological value of land is critical for sustainable land management. ELC provides landowners with detailed insights into habitat types and vegetation structures, empowering them to optimise their natural assets for carbon sequestration, flood management, or biodiversity conservation.
3. Nature-Based Restoration
From rewilding projects to green corridor planning, ELC equips restoration specialists with accurate data to design interventions that align with the local environment. High-resolution imagery ensures that even small-scale initiatives can be tailored for maximum ecological impact.
4. Urban Habitat Analysis
Urban environments pose unique challenges for habitat monitoring. ELC’s high-resolution imagery captures natural features in densely built-up areas, enabling planners to assess the biodiversity potential of spaces like residential gardens and parks.
5. Digital and Software Integrations
The data can enhance existing digital platforms that deal with natural landscape mapping. By incorporating ELC Mapping, lower-resolution systems can be transformed, offering users a more comprehensive and detailed understanding of their environment.
Addressing Customer Pain Points with ELC Mapping
The development of ELC Mapping directly addresses several long-standing challenges faced by ecologists and planners:
-
Lack of Unified Datasets
Historically, biodiversity assessments required expertise in reconciling datasets from different sources. ELC eliminates this hurdle by aggregating all necessary data into a single authoritative product. -
Time-Consuming Surveys
Baseline surveys often demand significant fieldwork. By providing a highly detailed dataset for desktop analysis, ELC minimises unnecessary site visits, focusing efforts where they are most needed. -
Low-Resolution Imagery
Open-source imagery frequently lacks the detail required for habitat classification. The 25cm resolution of ELC Mapping ensures no critical features are overlooked.
Future Prospects: A Tool for Decades
ELC Mapping is not merely a short-term solution. Its design aligns with the long-term monitoring requirements of environmental legislation, such as the UK’s mandate for 30-year BNG assessments. With OS’s established history and commitment to innovation, users can rely on the continuity and evolution of the dataset.
Furthermore, ongoing enhancements, such as incorporating UKHab Level 2 classifications, will expand its capabilities, enabling more granular ecological assessments.
Why Choose Ordnance Survey?
For over 230 years, Ordnance Survey has been the cornerstone of mapping and geospatial intelligence in Britain. The ELC Mapping initiative is a testament to its dedication to innovation and sustainability. By choosing OS, users gain access to:
- A trusted and authoritative provider with an unmatched legacy.
- Data that integrates seamlessly with modern technologies and workflows.
- A commitment to ongoing updates and advancements, ensuring users always work with the best tools available.
Enhanced Land Cover Mapping represents a significant leap forward in geospatial technology, combining high-resolution imagery, authoritative datasets and user-friendly formats. Its versatility addresses the needs of ecologists, developers, and urban planners, offering solutions to some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
As the demand for sustainable development grows, tools like ELC Mapping will become indispensable for making informed decisions that balance progress with conservation. By adopting this innovative dataset, professionals can not only streamline their workflows but also contribute to a more sustainable and biodiverse future.
The Enhanced Land Cover Mapping by Ordnance Survey is not just a product; it is a step toward transforming how we understand and interact with our environment. Whether you’re a policymaker, developer, or ecologist, this is a game-changing tool and drive a positive impact on the world around us.