Ordnance Survey's National Geographic Database (NGD) emerges as a solution for businesses and government institutions seeking streamlined access to important location information in the field of geospatial data. This comprehensive guide seeks to provide an in-depth introduction of OS NGD, breaking down its essential components, applications across sectors, implementation methodologies, and potential acceptance issues.
Download large scale Ordnance Survey maps here
Understanding OS NGD
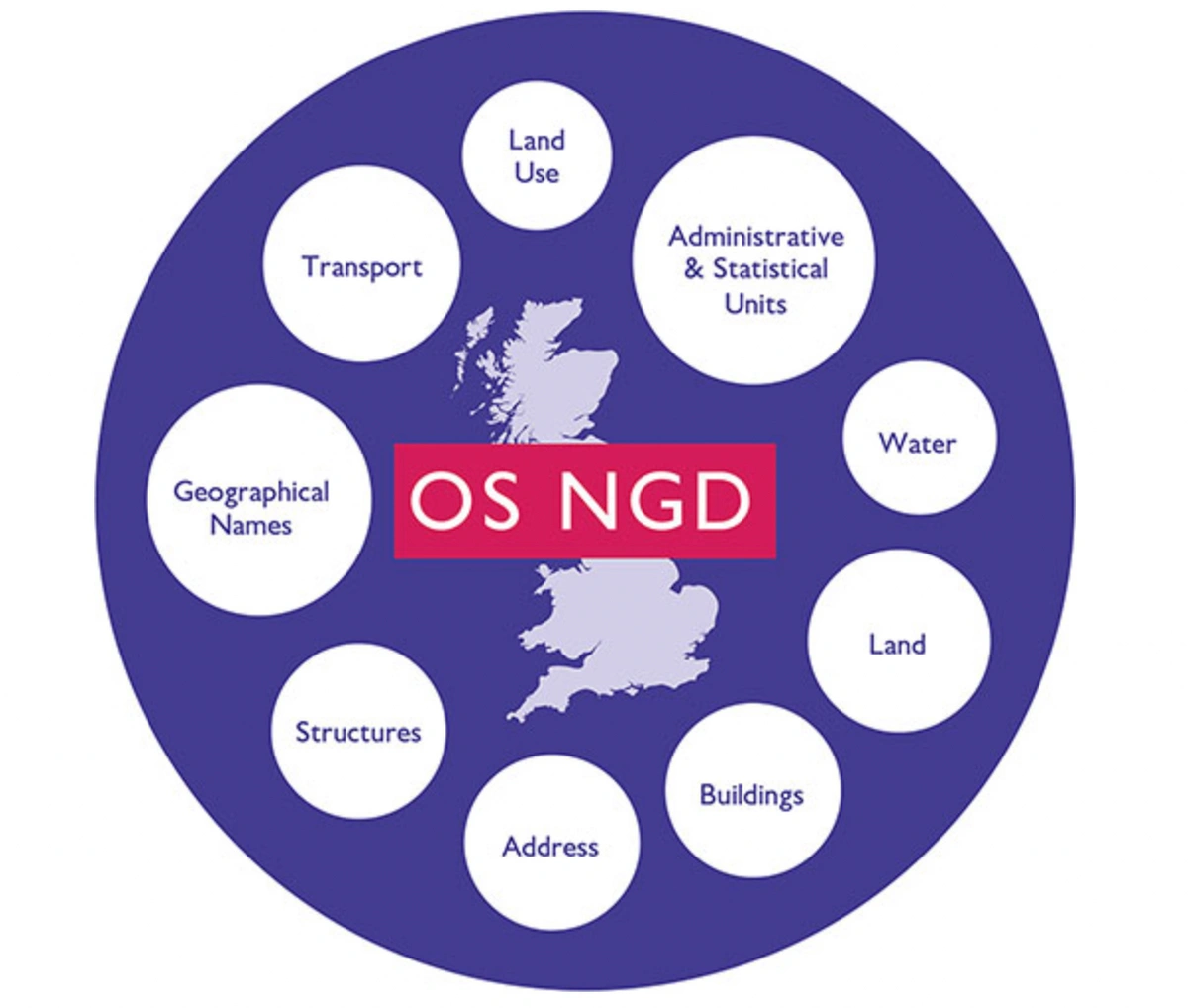
The OS National Geographic Database (OS NGD) is a centralised collection of all authoritative data related to the United Kingdom. OS NGD improves data richness, and streamlines the process of locating, packaging, and analysing critical data, such as address and building information, which is critical for emergency preparedness. It is organised into nine data themes and divided into collections including approximately 70 feature types:
- Address
- Administrative and Statistical Units
- Buildings
- Geographical Names
- Land
- Land Use
- Structures
- Transport
- Water
OS NGD Data Themes
Image provided by the OS
How is NGD different from the rest of OS data?
OS NGD data differs from our other offerings in that it is accessible from a single place, allowing customers to find relevant data without having to download full datasets. Its reduced data format is designed for efficient problem resolution and the creation of more intelligent solutions, allowing for faster loading and deployment. The geographic data for the United Kingdom is divided into nine themes, each of which includes collections and feature types. The Transport theme, for example, offers collections such as Routing and Asset Management, Transport Features, and Transport Network, as well as feature types such as Road Line, Road Track or Path, and Rail. Users can access individual aspects within a collection, such as Road Line, to tailor their data retrieval to specific needs.
What are the benefits of the National Geographic Database (NGB)?
Customers benefit from numerous main features of the OS National Geographic Database (NGD). Firstly, it increases the frequency of data updates, allowing users to access data themes that are updated daily via the new OS NGD APIs and OS Select+Build. Customers can choose and design their own data packages for the first time, personalising selections to their individual needs without having to filter out superfluous information. OS Select+Build's download service and the online access provided by OS NGD API - Features and OGC API - Tiles correspond to the most recent OGC standards, providing easier and more efficient data access. Customers will like the user-friendly data formats, such as GeoPackage, CSV, GeoJSON, and vector tiles. Improved data architectures, metadata, and documentation platforms make data more discoverable. OS NGD is created with future modifications in mind, and it is included in the Public Sector Geospatial Agreement (PSGA), providing free access to Public Sector organisations as well as commercial resale by OS Partners. Furthermore, the data is supplemented with attribution for easy navigation and searching.
Image provided by the OS
How can NGD be useful?
The OS National Geographic Database (OS NGD) is a critical resource for quickly retrieving geographic data. It provides a comprehensive database available via the OS Data Hub, with over 500,000 detailed features updated daily.The database, designed to satisfy the demands of government, emergency services, and the financial sector, includes addresses' highest and lowest floor levels, boosting risk assessment for fire, flood, and other risks. Furthermore, OS NGD assists urban planning activities by expanding the path network and incorporating new cycle lane and streetlight information for a sustainable, low-carbon future. Building upgrades in the database, such as age, material, and roof aspect details, make it easier to remodel homes with solar panels, insulation, and heat pumps.