When we look at design and engineering, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) maps serve as vital tools for professionals spanning a broad spectrum of disciplines, including architecture, civil engineering, urban planning and landscape design. A well-constructed CAD map offers much more than a basic layout; it provides a comprehensive, multi-layered representation of a project, delivering crucial insights that can save time, reduce costs, and enhance the accuracy of any design or construction endeavour.
Here are the top 7 features to prioritise when selecting professional CAD maps to ensure you're maximising the potential of your design tools:
Get Professional CAD Maps
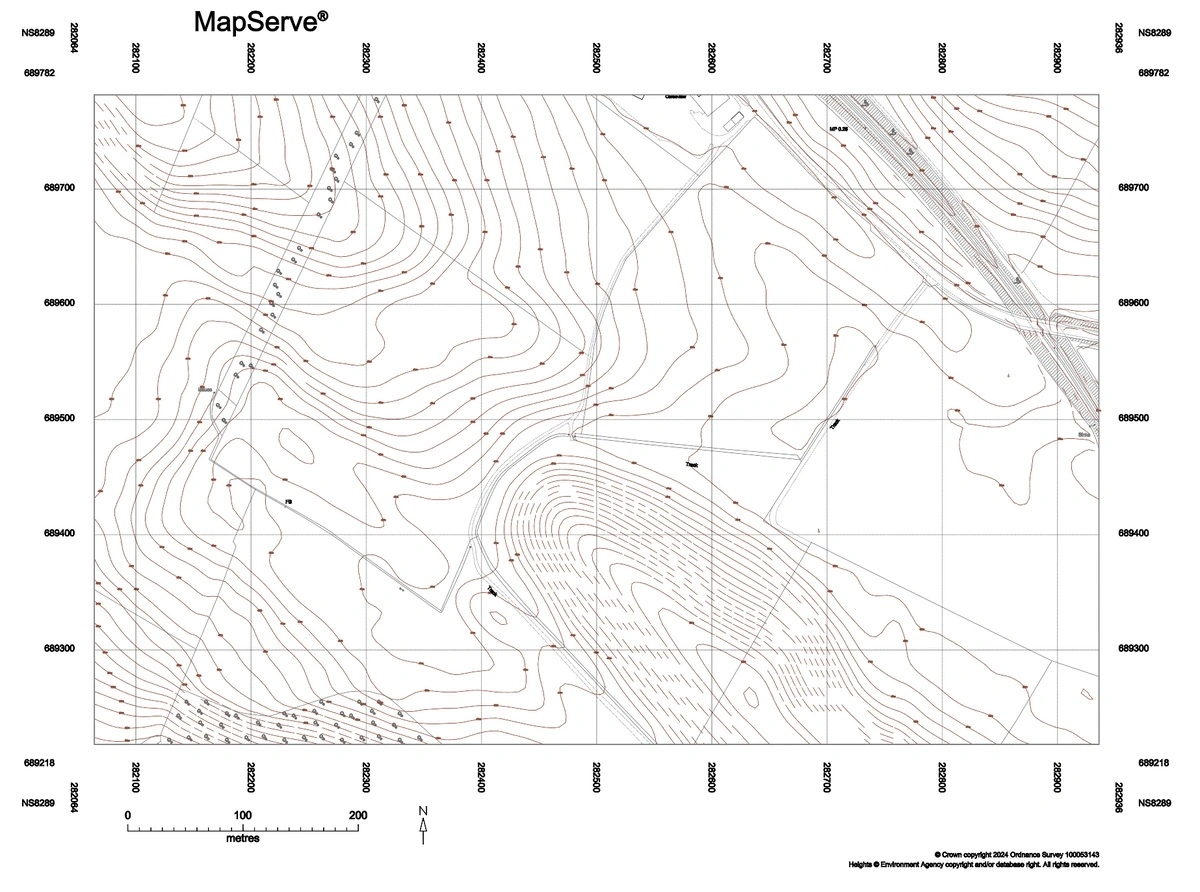
1. Topographic Data
The topography of a CAD map forms the bedrock of any effective design project. Accurate representation of the terrain, including elevation contours, slope gradients, and landform characteristics, is indispensable for understanding the physical context in which your project will be realised. A topographic map aids in the meticulous planning of elements such as drainage systems, cut-and-fill calculations and the positioning of structures relative to natural landforms. This ensures your designs are not only aesthetically pleasing but also structurally sound and sensitive to the surrounding environment.
For example, when working on a project in a hilly area, precise topographical data allows for the accurate design of roads that minimise steep gradients, thereby reducing construction costs and improving safety.
Topographic CAD map sample
2. Customisable Layers
A robust CAD map should offer the capability to work with customisable layers. This feature is essential for managing complex designs, as it enables you to isolate and focus on specific aspects of your project, such as utilities, transportation networks, or environmental features, without the distraction of other elements. Customisable layers also support collaborative workflows, allowing different team members to work on specific layers independently, each contributing their specialised knowledge to the overall project.
In large infrastructure projects, for instance, the ability to separate electrical, water, and gas utilities into different layers can significantly streamline the planning and coordination process, reducing the risk of conflicts during construction.
3. High-Resolution Data
The importance of resolution in CAD maps cannot be overstated, particularly when precision is paramount. High-resolution data ensures that every element of your map is rendered with exceptional detail, whether you're working on intricate architectural designs or expansive urban planning projects. High-resolution maps facilitate the integration of additional datasets, such as geographic information systems (GIS) and satellite imagery, providing a more comprehensive view of the project area.
For projects involving detailed environmental assessments, high-resolution data is crucial for identifying sensitive areas, such as wetlands or protected habitats, which might impact design decisions and regulatory approvals.
4. Scalability
Scalability is a critical feature for any professional CAD map. As your project progresses, the ability to scale your map up or down without losing detail or context is essential. A scalable CAD map allows you to seamlessly transition from a broad overview to detailed sections, maintaining the accuracy and relevance of your design across various scales, from small-scale residential developments to large-scale infrastructure projects.
For example, in urban planning, the ability to zoom out to view an entire city layout and then zoom in to focus on a single neighbourhood or street enables more precise and contextually aware decision-making.
5. Precision Measurement Tools
Precision is the cornerstone of any successful design or construction project. Professional CAD maps should come equipped with advanced measurement tools that allow for the accurate calculation of distances, areas, volumes, and other critical metrics. These tools are invaluable during both the planning and execution phases, helping to ensure that your designs are implemented correctly and efficiently, thus minimising errors and avoiding costly rework.
In civil engineering, for instance, precise measurement tools are essential for calculating the volume of earthworks, ensuring that cut-and-fill operations are balanced, thereby reducing material costs and environmental impact.
6. Integration with Other Software Platforms
In today's highly interconnected world, no software tool operates in isolation. Your CAD map should be capable of easy integration with other essential software platforms, such as GIS, Building Information Modelling (BIM) and project management tools. This integration is crucial for streamlining workflows, enhancing data accuracy and ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the most current information. The ability to import and export data across platforms is vital for maintaining consistency and fostering collaboration throughout the project lifecycle.
For instance, the integration of BIM with CAD maps enables architects and engineers to visualise how a building will interact with the surrounding environment, ensuring that designs are not only structurally sound but also contextually appropriate.
Diagram provided by Monarch Innovation
7. User-Friendly Interface
Even the most sophisticated CAD map is of limited value if it is difficult to use. A user-friendly interface is essential for maximising productivity and ensuring that both novice and experienced users can fully utilise the map's features. This includes intuitive navigation, customisable toolbars, and straightforward commands that facilitate the design process.
A well-designed interface should also offer advanced features such as contextual help, automated error checking, and the ability to create custom workflows, which can significantly reduce the learning curve and improve overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Selecting the right CAD map for your project is not merely a matter of choosing a tool—it is an investment in the success of your design and construction efforts. By prioritising these seven features — topography, customisable layers, high-resolution data, scalability, precision measurement tools, integration with other software platforms and a user-friendly interface—you can ensure that your CAD maps not only meet but exceed the rigorous demands of professional projects.
For additional insights on selecting quality maps and avoiding common pitfalls, check out this helpful YouTube guide on "How to Tell a 'Bad Map' from a 'Good Map' and Save Hours" which can further enhance your understanding of what to look for in professional CAD maps.
Whether you are designing a skyscraper, planning a new urban development, or mapping out a landscape, the right CAD map can be the difference between a successful project and one fraught with challenges. Investing in the best tools available is a step towards realising your vision with precision, efficiency and confidence.