Optimising Architectural Site Analysis with Topographical Maps
Topographical mapping is an indispensable tool in the arsenal of architects, surveyors, and planners. It offers a comprehensive view of the natural terrain, providing invaluable insights into land features that are crucial for strategic decision-making in architectural site analysis. In this blog post, we delve into the importance of topographical maps in architectural site analysis, exploring their various uses and benefits for professionals in the building industry.
Download Topographical Maps of the UK Here
Understanding Topographical Mapping
Topographical maps, also known as topo maps, are detailed representations of the Earth's surface, showing elevation contours, terrain features, and land characteristics with precision. These maps are created through topographic surveying techniques, such as aerial photography, LIDAR scanning, and ground surveys, which capture data points to create accurate representations of the landscape.
What is an Architectural Site Analysis?
Architectural site analysis is an important method used by architects, urban planners, and designers to evaluate and comprehend the characteristics of a site when a building or development project is proposed. It entails collecting data and information on the site's physical, environmental, cultural, and social characteristics to successfully inform the design process. This study enables architects to make informed decisions about site suitability, design considerations, and potential obstacles or opportunities, ensuring that the final design blends seamlessly with its surroundings and fits the needs of its users.
The site analysis is completed at the early stages of a project. In a professional setting, it often occurs during Stage 2 (Concept Design) of the RIBA Plan of Work. Site information, including site surveys, is sourced, therefore topographical maps are required throughout this step.
Uses of Topographical Maps in Architectural Site Analysis
Site Selection and Evaluation
Topographical maps are critical instruments in the process of site selection and appraisal for architectural projects, especially for professionals working in the United Kingdom. Architects, surveyors, and planners rely largely on the information supplied by these maps to carefully evaluate potential building sites across varied terrain. They carefully analyse a variety of characteristics, such as slope gradients, elevation differences, and soil composition, all of which are critical in establishing a site's viability and suitability for development. Through a thorough examination of topographical data, these professionals can discover suitable places that correspond with the natural qualities of the land, reducing environmental effect and assuring the long-term sustainability of architectural developments in the UK. This reliance on topographical mapping emphasises its critical role in influencing strategic decision-making processes and eventually altering the built environment to achieve both functional and environmental goals.
Grading and Earthwork Planning
Topographic maps are vital resources for architects working in the United Kingdom, providing a wealth of critical information for grading and earthwork planning during the pre-construction phase of architectural projects. Architects use these highly detailed maps to carefully examine and determine the best location of buildings and infrastructure within prospective development areas. Professionals can strategically and efficiently plan earthwork activities by carefully analysing elevation contours and slope gradients offered by topographical data. This rigorous design not only allows for appropriate drainage and reduces soil erosion, but it also ensures that the land is used effectively while keeping building costs low. Architects in the United Kingdom can streamline the pre-construction phase of architectural projects by strategically utilising topographical mapping, resulting in the successful and sustainable realisation of built environments that meet the diverse needs of communities across the country.
Infrastructure Design and Development
In addition to playing an important part in site planning, topographical maps are invaluable resources for informing the design and development of infrastructure projects, which is critical for architects working in the UK. Civil engineers, in particular, rely significantly on the rich topographical data supplied by these maps to meticulously build roads, utilities, and drainage systems that blend smoothly with the surrounding topography. Engineers can improve the functioning and resilience of urban environments across the UK by incorporating topographical insights into the infrastructure design process, boosting efficient transport networks and reducing flood hazards. This intentional incorporation of topographical mapping into infrastructure design not only ensures the long-term viability of urban developments, but also helps to create safe, resilient, and livable communities for both residents and visitors.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Topographical mapping is an essential technique for comprehensively assessing the environmental impact of architectural projects, which is an important concern for architects working in the UK. Environmental planners and sustainability consultants use the rich data offered by these maps to undertake thorough assessments of the potential effects of development on sensitive ecosystems and natural habitats within project regions. Professionals can identify ecologically sensitive locations and develop personalised mitigation measures to reduce negative impacts on the surrounding environment by meticulously analysing topographical data. This strategic approach not only assures compliance with environmental rules, but it also promotes responsible development practices that prioritise the preservation and conservation of the natural environment. By adding topographical mapping into the environmental impact assessment process, UK architects can actively contribute to the building of sustainable built environments that coexist harmoniously with their surroundings for the benefit of current and future generations.
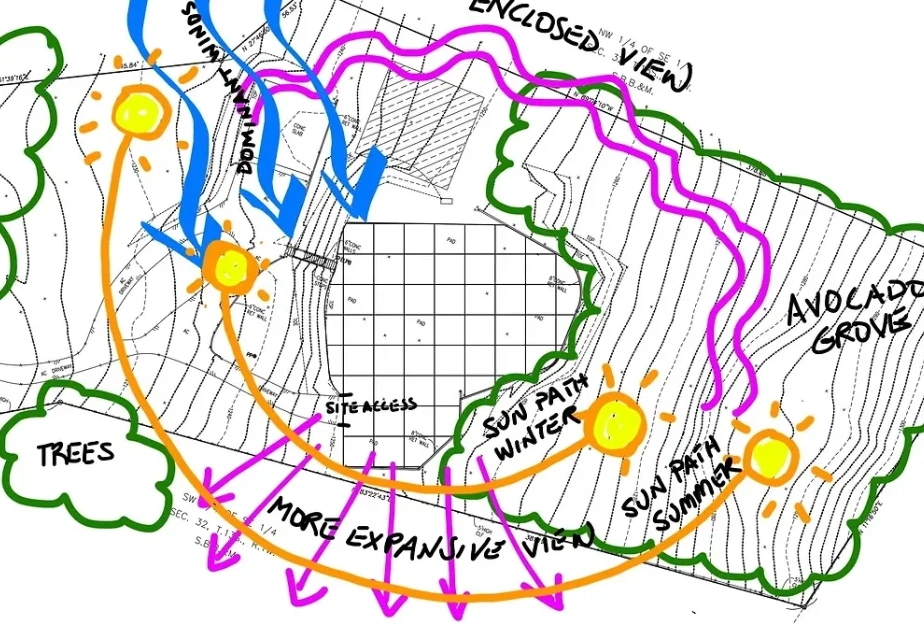
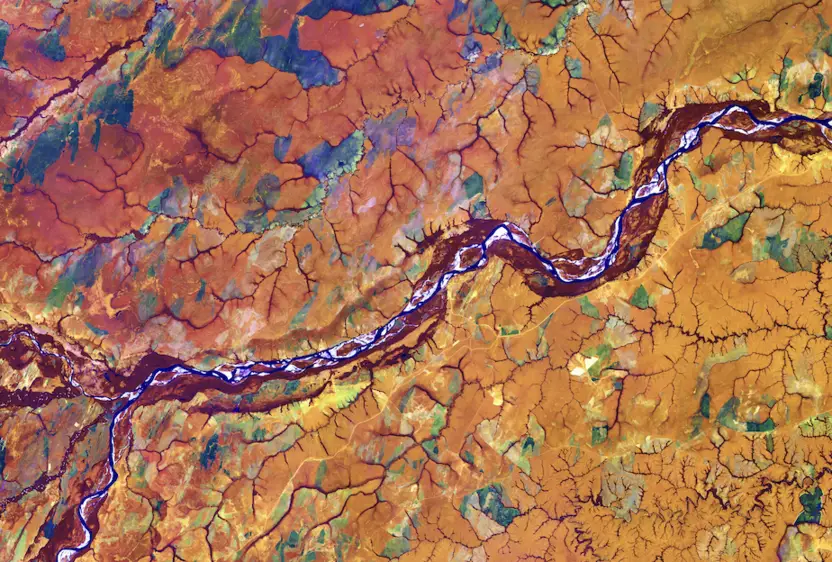
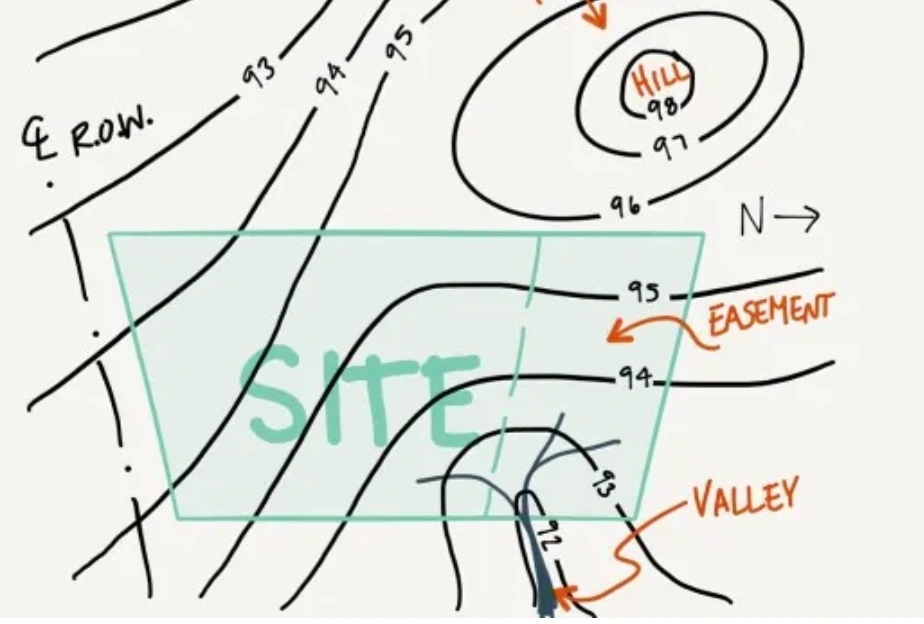
Architectural Site Analysis using topographical maps (Images provided by Archi Monarch)
How Does Topography Influence Architecture Design?
Site Suitability
Topography dictates the suitability of a site for construction. Steep slopes, uneven terrain, or unstable ground may pose challenges for building foundations and structural stability. Architects must carefully assess topographical features to select suitable sites and design appropriate foundation systems.
Building Placement
The natural contours of the land can influence the placement and orientation of buildings. Architects may choose to position structures to take advantage of scenic views, natural light, or prevailing winds, while also considering factors such as drainage and soil stability.
Structural Design
Topography affects the structural design of buildings, particularly in hilly or mountainous regions where structures must withstand the forces exerted by gravity, wind, and seismic activity. Architects and engineers must account for these factors in designing robust and resilient structures.
Access and Circulation
Topographical features such as hills, valleys, and water bodies can impact site accessibility and circulation. Architects must plan for efficient transportation routes, pedestrian pathways, and vehicular access to ensure ease of movement within the site and minimize environmental disruption.
Environmental Considerations
Topography influences microclimatic conditions, such as temperature variations, wind patterns, and precipitation levels, which can affect building performance and energy efficiency. Architects may incorporate passive design strategies, such as natural ventilation and solar orientation, to mitigate environmental impacts and enhance occupant comfort.
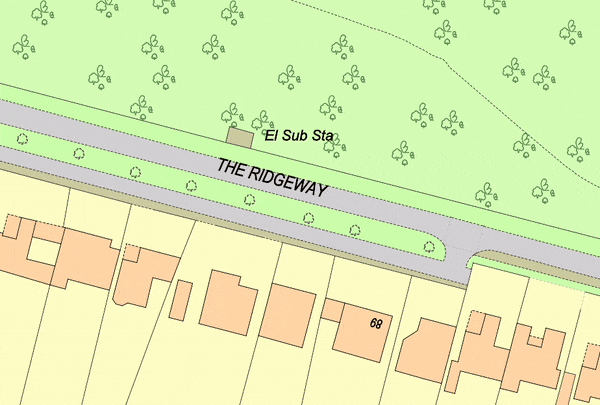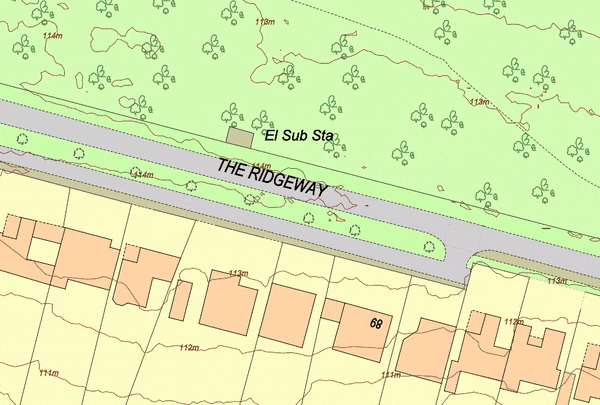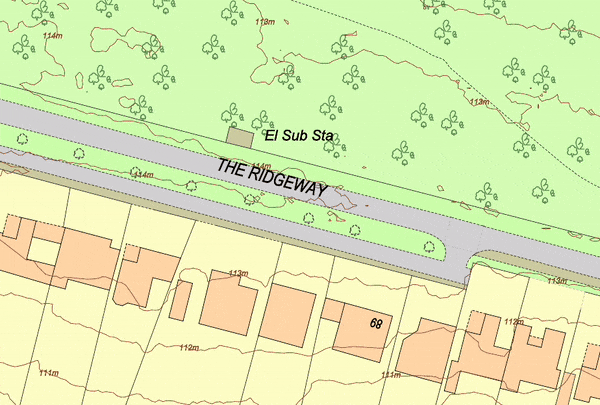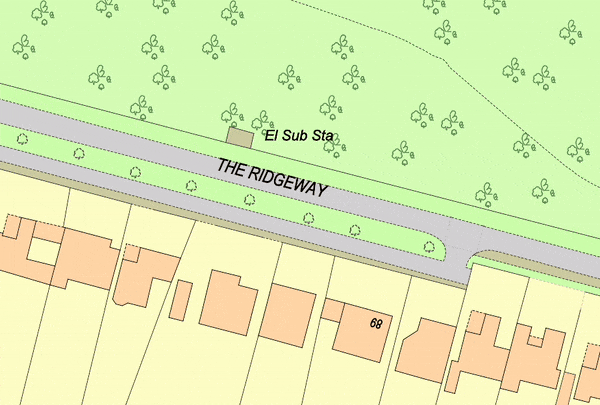
Topographical Map showing 1m contours provided by MapServe®
Integrating Topographic Maps into Site Planning
Site Constraints
Topographic maps give architects and planners with an efficient tool for identifying site limits. These maps provide extensive information about elevation, slope, and land contours, allowing professionals to identify places that may pose issues or limitations. Early understanding of site limits enables architects to make educated decisions that maximise the site's usability and functionality.
Drainage Patterns
The capacity to thoroughly examine drainage patterns is an essential component of incorporating topographic maps into site planning. These maps depict the movement of water around the property, highlighting natural drainage pathways and regions prone to water retention. By analysing these patterns, architects may create personalised drainage systems that efficiently reduce concerns like flooding and erosion.
Accessible Pathways
Topographic maps are useful for planning accessible pathways within the site, as they provide information about terrain, gradients, and slopes. This data is critical for building pathways that meet accessibility standards, assuring the safety and inclusivity of all users. Architects can design pathways that are easy to navigate and meet a variety of mobility needs by meticulously analysing topographic elements.
Building Placement
Including topographic maps in the site planning process allows architects to optimise building placement depending on the site's natural features. Architects may discover optimal construction locations by analysing elevation and slope data, allowing for more efficient site use while reducing the need for substantial earthwork and levelling. This strategic approach improves design efficiency while preserving the site's natural characteristics.
Topographical Map showing 1m contours of an area in Scotland, by MapServe®
To summarise, topographical mapping is important in architectural site analysis because it provides significant information for site selection, grading, infrastructure design, and environmental assessment. Topographical maps help architects, surveyors, and planners make educated judgements and guarantee that architectural projects are completed successfully. Topographical mapping insights can help experts in the building sector design sustainable, safe, and ecologically responsible constructed environments that improve community quality of life.